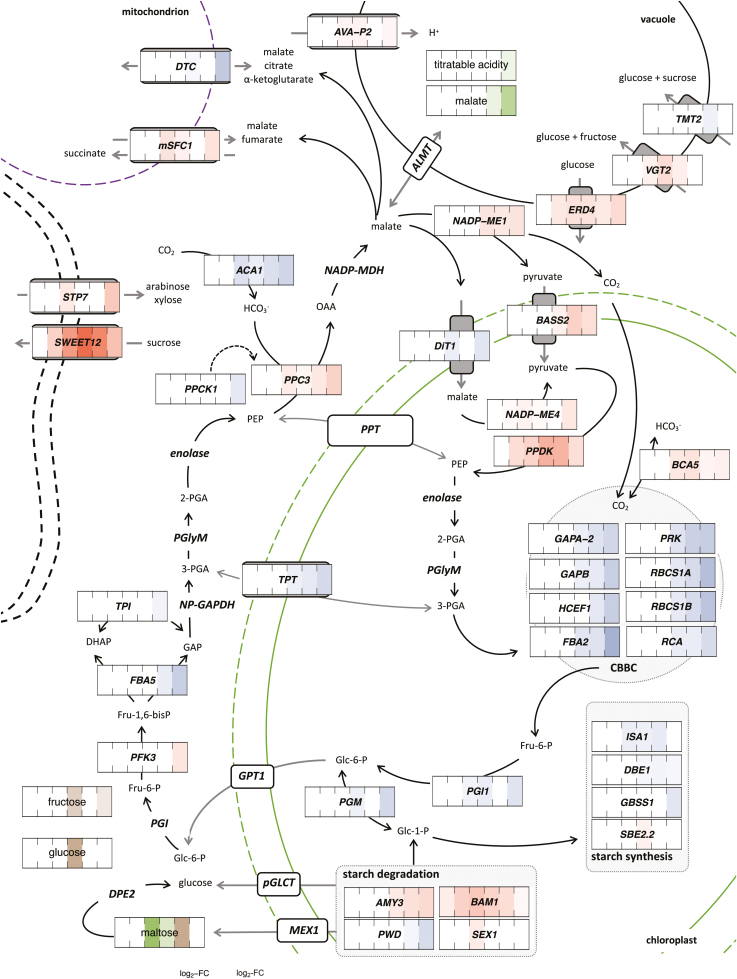
Fig. 2.
Exogenous ABA altered the transcript levels of core CAM genes and genes of related pathways, correlating with altered levels of selected metabolites in Talinum triangulare. Transcript abundances and metabolite amounts are expressed as log2-fold changes of ABA-treated compared with mock-treated leaves on blue–red and yellow–green scales, respectively (expression, n=2; metabolites, n=4). Only genes with significantly different transcript abundances (DESeq with Benjamini–Hochberg correction, q-value ≤0.01) and significantly altered temporal patterns (maSigPro with Benjamini–Hochberg correction, q-value ≤0.01 and R2>0.85) are shown. The significance level for metabolites was 0.05 after Benjamini–Hochberg correction. Substrate conversions are depicted with solid lines, post-translation regulations with dashed lines, and transport processes are shown in grey. Genes whose involvement in the depicted pathways is expected are also included. Protein subcellular localization is based on prediction from Beta vulgaris (TargetP). 1,3-BPG, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; 2-PGA, 2-phosphoglycerate; 3-PGA, 3-phosphoglycerate; CBBC, Calvin–Benson–Bassham cycle; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; Fru-6-P, fructose-6-phosphate; Fru-1,6-bisP, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; GAP, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; Glc-1-P, glucose-1-phosphate; Glc-6-P, glucose-6-phosphate; OAA, oxaloacetate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PGlyM, phosphoglycerate mutase.