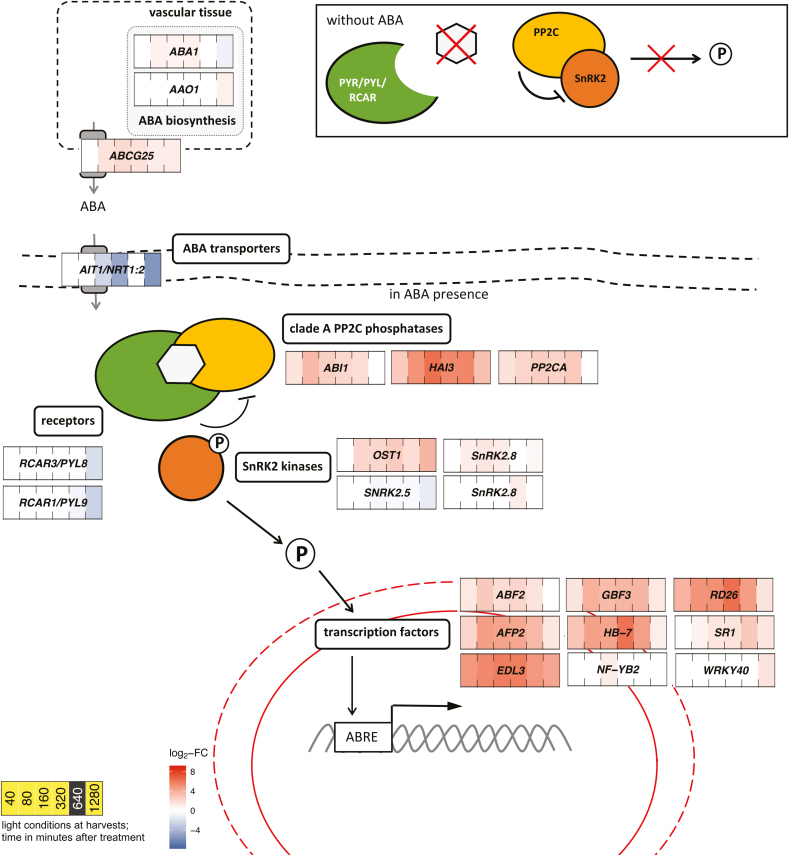
Fig. 3.
Transcript levels of genes involved in ABA signalling and biosynthesis were influenced by exogenous ABA in Talinum triangulare. Transcript abundances are expressed as log2-fold changes of ABA-treated compared with mock-treated leaves (n=2). Only genes with significantly different transcript abundances (DESeq with Benjamini–Hochberg correction, q-value≤0.01) and significantly altered temporal patterns (maSigPro with Benjamini–Hochberg correction, q-value≤0.01 and R2>0.85) are shown. The core signalling pathway comprises PYR/PYL/RCAR receptors, clade A phosphatases PP2C, and SnRK2 kinases. In the absence of ABA, PP2C phosphatases bind SnRK2s and prevent them from phosphorylating downstream targets. Upon binding of ABA to the receptors, they capture PP2Cs, releasing phosphorylated SnRK2s. Targets of SnRK2s include transcription factors in particular, many of which regulate gene expression through binding to ABA-responsive element (ABRE) motifs in promoter sequences of target genes. OST1 is involved in the control of stomatal movement. P, phosphorylation.