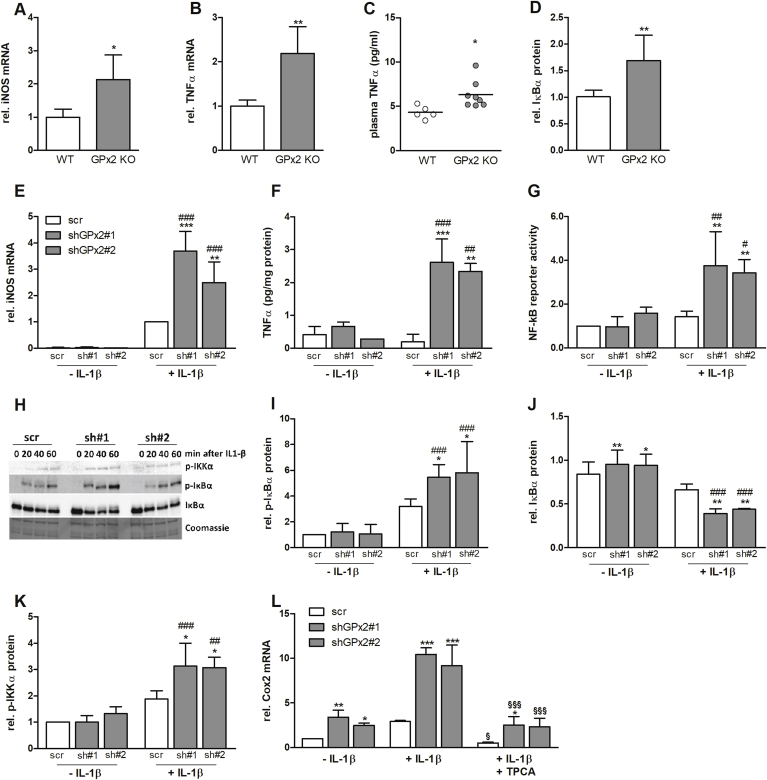
Fig. 1.
Deletion of GPx2 enhances inflammatory protein expression and NF-κB activity in vivo and in vitro. In the intestine of WT and GPx2 knockout (GPx2 KO) mice, mRNA levels of iNOS (A) and TNF-α (B) were analyzed by qPCR and normalized to Rpl13a and Epcam. Plasma levels of TNF-α were analyzed by ELISA (C) and intestinal protein levels of IκBα were analyzed by Western blot and normalized to β-actin (D). In HT-29 cells, stable kds were generated using two different shRNA constructs against GPx2 (sh#1 and sh#2) and compared to cells expressing a non-targeting shRNA sequence (scr). All cells were supplemented with 50 nM sodium selenite for 72 h and stimulated with 1 ng/mL IL-1β. After 3 h of IL-1β stimulation, mRNA levels of iNOS (E) were measured by qPCR and secretion of TNF-α into the medium was measured by ELISA after 4 h of IL-1β stimulation (F). An NF-κB reporter gene assay was performed with and without IL-1β stimulation for 24 h and normalization to Renilla luciferase activity for transfection efficiency (G). Protein levels of IκBα, p-IκBα, and p-IKKα were analyzed at different time points as indicated (H). Quantification was performed at 40 min after IL-1β stimulation for IκBα and p-IκBα (I and J) and after 20 min for p-IKKα (K). COX-2 mRNA was analyzed after 3 h of IL-1β stimulation, with or without pretreatment with 20 μM TPCA for 1 h (L). Data are given as means + SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs. respective WT or scr control, #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.001 vs. respective unstimulated control (IL-1β); and §p < 0.05; §§§p < 0.001 vs. +IL-1β analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post-test.