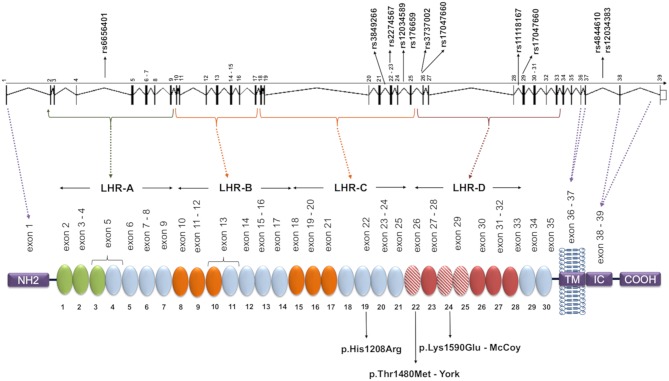
Figure 1.
CR1 gene and protein structure and localization of the investigated SNPs. Each circular block represents a SCR (short consensus repeat, numbered 1–30), encoded by the exons 2–35, listed immediately above. There are three C4b binding sites (SCR 1-3, 8-10, and 15-17, in green and orange) and two C3b binding sites (SCR 8-10 and 15-17, both in orange). SCRs 22-28 bind C1q, MBL, and ficolins, and SCRs 22, 24, and 25 (red dashed blocks) carry Knops blood group antigens. The SNPs analyzed in this study are indicated in the gene, and the amino acid substitutions resulting from polymorphisms located in exons are indicated on the protein. The dashed lines indicate coding exons of the main parts: the aminoterminal region (NH2, exon 1), transmembrane domain (TM, exons 36-37), the intracytoplasmic carboxi-terminal domain (IC COOH, exons 38-39), and the four long homologous repeats (LHR), responsible for complement decay-accelerating, and cofactor activities (exons 1-7, 8-14, 15-21, 22-28). The functional sites in 8-10 and 15-17 are nearly identical. Repeats in green are required for C4b binding and decay-accelerating activity, while those in orange are required for C3b and C4b binding and cofactor activity [adapted of (25)].