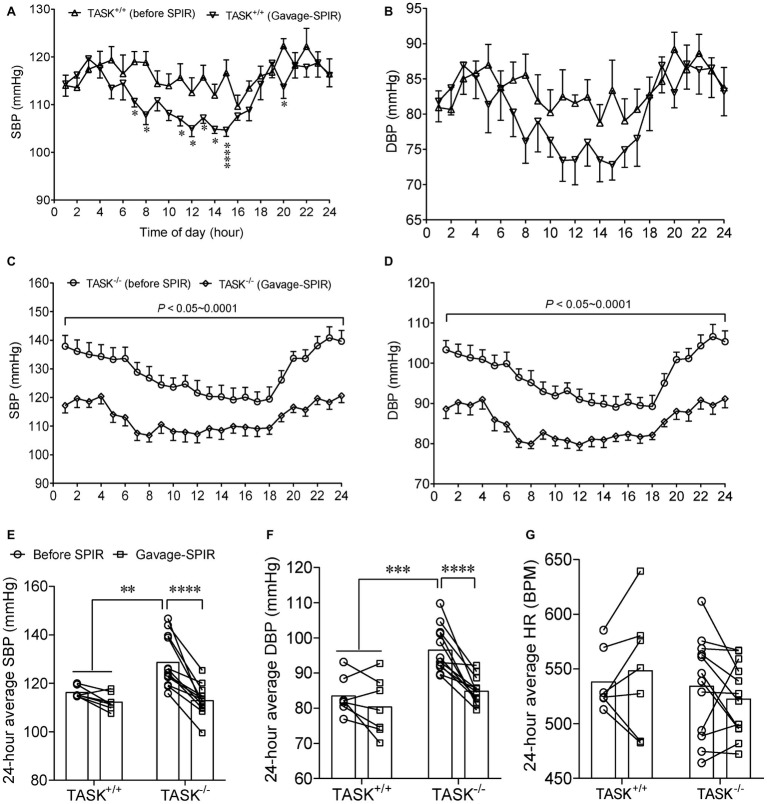
Figure 3.
Effect of oral administration of SPIR on arterial pressure. The MR antagonist SPIR was administered via oral gavage once daily for 7 days in TASK+/+ (n = 7) and TASK−/− mice (n = 12). (A,B) Administration of SPIR produced mild decrease in SBP only at specific time points and no obvious decrease in DBP in TASK+/+ mice. *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001 as indicated by two-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD post hoc test. (C,D) After treatment with SPIR, SBP and DBP were significantly lowered at each time point over 24 h in TASK−/− mice. (E–G) Application of SPIR markedly lowered 24-h average SBP and DBP in TASK−/− mice, with insignificant changes in TASK+/+ mice. No significant difference was observed in HR between two genotypes after MR blockade. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 as indicated by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. MR, mineralocorticoid receptors; SPIR, spironolactone.