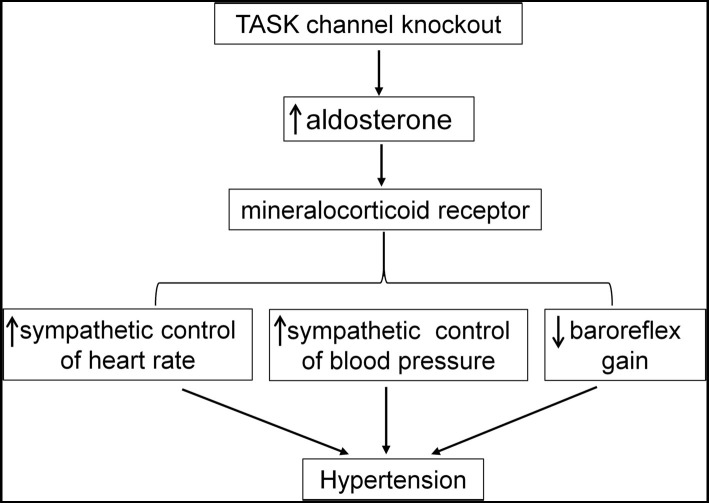
Figure 8.
Summary of the mechanism underlying hyperaldosteronism-associated hypertension. Genetic deletion of TASK channels results in hyperaldosteronism. Then, overactivation of MR by Aldo contributes to enhanced sympathetic control of HR and BP and impairment of baroreflex, finally leading to elevated BP.