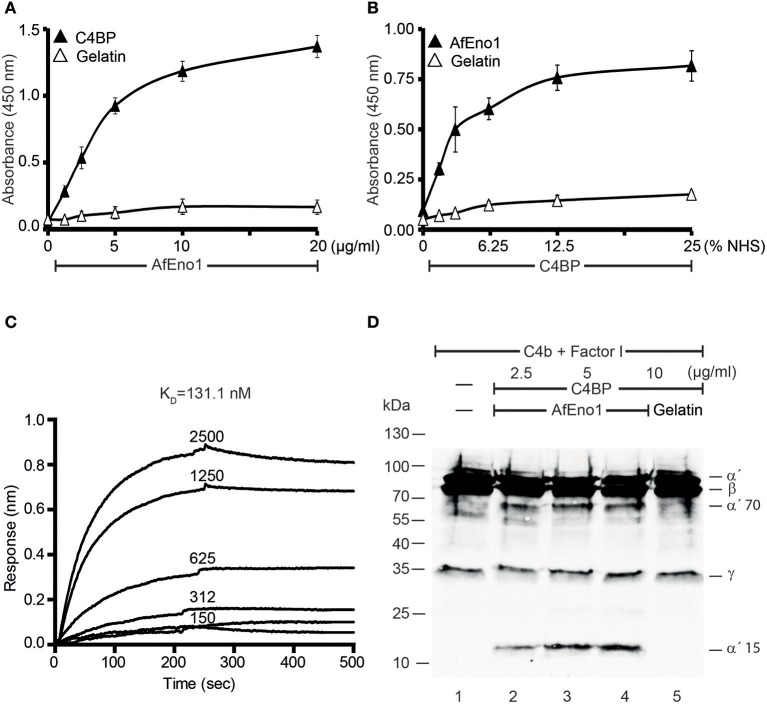
Figure 3.
C4b binding protein (C4BP) binds to Aspergillus fumigatus enolase (AfEno1), and AfEno1-bound C4BP retains regulatory activity. (A) AfEno1 was immobilized onto a microtiter plate overnight, and C4BP at increasing amounts was added. After washing, bound C4BP was detected with goat human C4BP antiserum. C4BP showed no binding to gelatin. (B) Plasma-derived C4BP binds to AfEno1 dose dependently. Normal human serum (NHS) (10 mM EDTA) at different concentrations was added to immobilize AfEno1, and bound C4BP was detected as above. (C) The binding affinity of C4BP with AfEno1 was evaluated by biolayer interferometry. C4BP at the indicated concentrations (150, 312, 625, 1,250, and 2,500 nM) was bound to AfEno1 immobilized on Ni-NTA sensor surfaces. For each concentration, the association was followed for 250 s, and upon removal of the analyte, the dissociation followed another 250 s. C4BP binds to AfEno1 with a KD = 131.1 nM. (D) C4BP bound to AfEno1 retained cofactor activity. C4BP at indicated amounts was attached to immobilized AfEno1. After washing, C4b and factor I were added for 4 h, and the proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. After being transferred to the membrane, C4b cleavage products were visualized by western blotting with goat human C4 antiserum. C4BP bound to AfEno1 assisted in cleavage of C4b by factor I, and C4b cleavage products α′70 and α′15 were identified dose dependently (lanes 2–4). No C4b cleavage products were observed in the negative control gelatin (lane 5). (A,B) Are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (D) Represents one of three independent experiments.