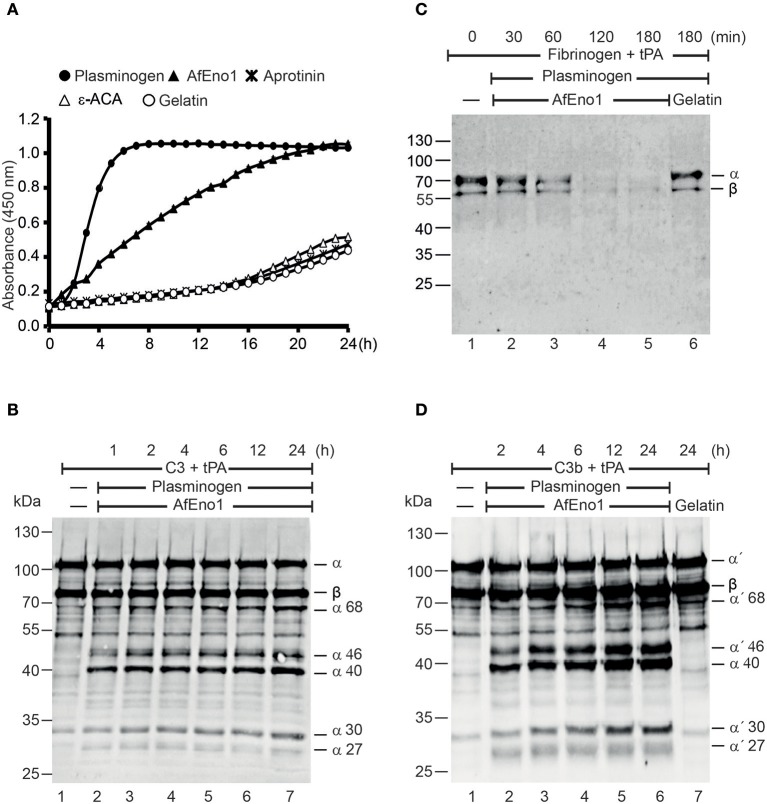
Figure 5.
Plasminogen bound to Aspergillus fumigatus enolase (AfEno1) is available for the activators. (A) Plasminogen was added to immobilized AfEno1 on a microtiter plate for 1 h. After washing, the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and the chromogenic substrate S-2251 were added. The plasmin activity was photometrically red at 405 nm for every 30 min, over 24 h. AfEno1-bound plasminogen was converted to plasmin, which cleaved the substrate S-2251 time dependently. ε-Aminocaproic acid (ε-ACA) and aprotinin inhibited S-2251 cleavage. No cleavage of S-2251 occurred in the negative control gelatin. (B) Fibrinogen and tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) were added to the preformed AfEno1–plasminogen complex. The reactions were stopped at indicated time points, and the proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Fibrinogen degradation was visualized by Western blotting with a rabbit human fibrinogen antiserum. AfEno1-bound plasminogen was activated to plasmin which cleaved fibrinogen (lanes 2–5). No fibrinogen degradation was visualized in the negative control gelatin (lane 6). (C) C3 and tPA were added to the preformed AfEno1–plasminogen complex. The reaction was stopped at different time points, and the proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE. C3 degradation products were visualized by western blotting with goat human C3 antiserum. Plasminogen bound to AfEno1 was activated to plasmin which cleaved C3 (lanes 2–7). (D) AfEno1 was immobilized on a microtiter plate, and after washing, C3b and tPA were added. The reaction was stopped indicated time points, and the proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. C3b cleavage products were determined as above. AfEno1-bound plasminogen was converted to active plasmin which degraded C3b (lanes 2–7). One representative result of three independent experiments is shown in each panel.