Fig 1.
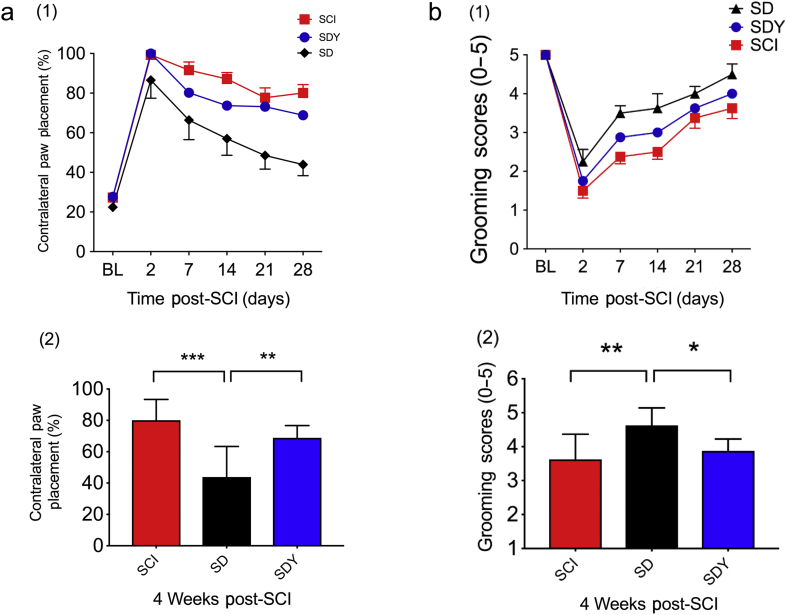
Dexmedetomidine (DEX) improves neurological outcomes 4 weeks after spinal cord injury (SCI). SD, SCI+DEX; SDY, SCI+DEX+yohimbine (Yoh). (a) In paw placement test, rats with right C5 injury had less contralateral forepaw placement for weight support, which suggests better recovery in the ipsilateral forelimb after DEX treatment (SD) over a 4-week period compared with vehicle control (SCI) (1). Between SCI and SD groups, there are significant DEX treatment effects (F [1; 120]=40.8; P<0.0001) in percentage of contralateral paw placement using two-way analysis of variance (anova) with repeated measures. In SCI rats pretreated with the α2 antagonist Yoh before DEX administration (SDY), the functional benefit of DEX was partially reversed (SD vs SDY [F {1; 96}=13; P=0.0005], two-way anova with repeated measures). At the end of 4 weeks after SCI (2), there was a significant improvement in the SD group compared with SCI (***P<0.0001, one-way anova with Tukey's test). Such functional improvement was partially reversed by Yoh pretreatment (**P=0.0099; one-way anova with Tukey's test) (n=8–10 in each group). (b) In a grooming test, rats with right C5 SCI had better grooming scores in the right upper limb after DEX treatment (SD) over a 4-week period compared with the vehicle control (SCI) (1). Between the SCI and SD groups, there was a significant treatment effect (F [1; 14]=16.5; P=0.0012) by two way-anova with repeated measures. In a separate group, SCI rats were pretreated with the α2 antagonist Yoh before DEX administration, and the functional benefit of DEX was partially reversed (SD vs SDY [F {1; 14}=4.8; P=0.0459], two-way anova with repeated measures). At the end of 4 weeks after SCI (2), there was a significant improvement in the SD group compared with SCI (**P=0.005; one-way anova with Tukey's test). The functional improvement was partially reversed by Yoh pretreatment (*P=0.0366; one-way anova with Tukey's test) (n=8–10 in each group). BL, baseline.