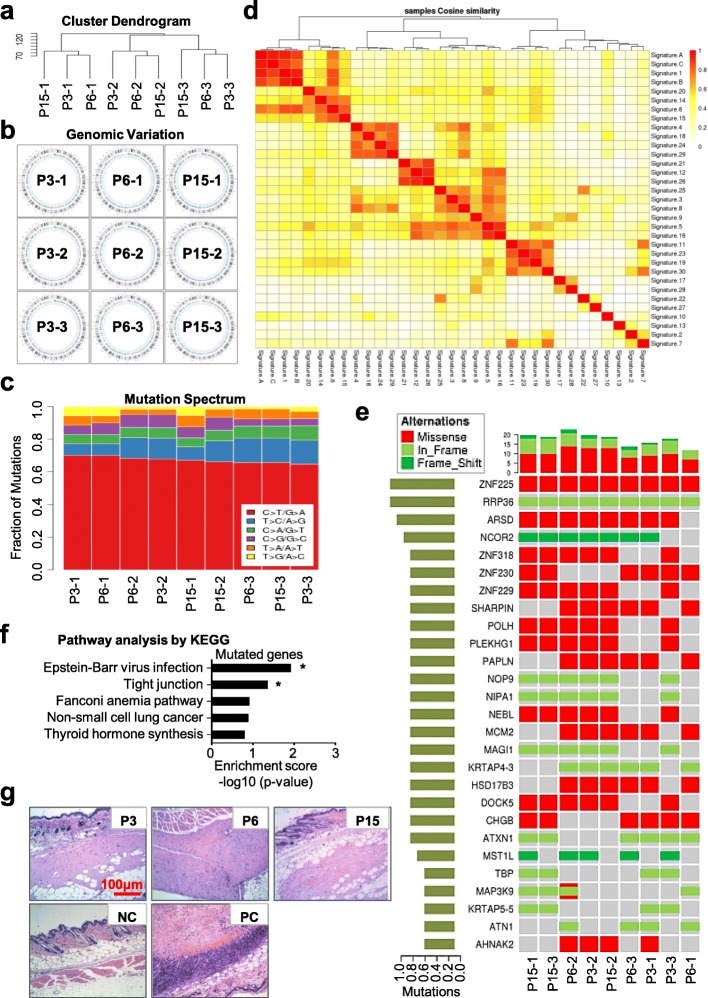
Fig. 3.
Safety evaluation of hUC-MSCs at various passages by mutation spectrum and tumor formation analysis. a Hierarchical clustering analysis of hUC-MSCs at various passages (P3, P6, P15) based on SNP data of 334,378 exons. b Cumulative somatic mutation analysis of genetic mutations in hUC-MSCs at various passages (P3, P6, P15) by Circos software. c Fraction of high-frequency SNV mutations among the indicated hUC-MSCs at various passages (P3, P6, P15). d The nonnegative matrix factorization algorithm (NMF) showed that the point mutations were refined into 96 subsets based on the location of 1 bp base around the upstream and downstream. Then, unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis of the different signatures (signature A, B, C) with the 30 kinds of characteristics of somatic point mutations. e High-frequency mutation analysis of hUC-MSCs at various passages (P3, P6, P15) including single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and INDEL mutations by using the MuSic test. f Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis of the genes with high-frequency mutations in hUC-MSCs at various passages (P3, P6, P15) by using PathScan software. g Tumorigenicity assay of hUC-MSCs at various passages (P3, P6, P15) by subcutaneous injection of the 1.0 × 107 hUC-MSCs mixed with Matrigel into nude mice. Mice with Matrigel injection were used as the negative control (NC), mice with 1.0 × 106 Hela cells mixed with Matrigel injection were used as the positive control (PC). H&E staining was performed for tumor structure detection (scale bar = 100 μm)