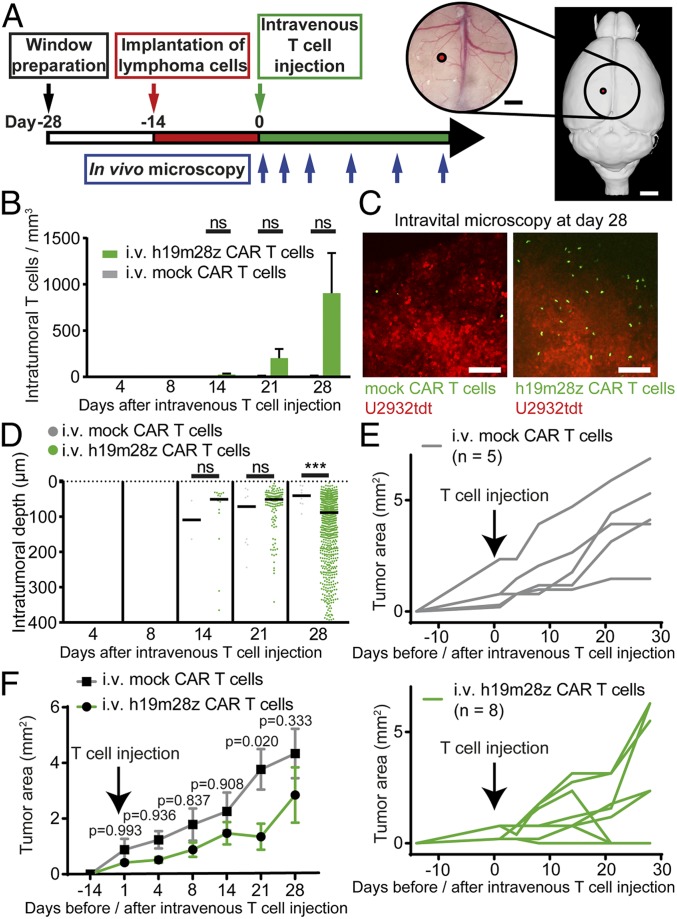
Fig. 2.
After i.v. injection, intratumoral h19m28z CAR T cells are present in low numbers without a sustained effect on tumor growth for the majority of treated animals. (A) Schematic representation illustrating experimental design. Right panel created with 3dBAR/SBA (53–55). (B) Intratumoral mock or h19m28z CAR T cell numbers after i.v. injection (quantification of 1 to 3 3D ROIs per mouse per time point depending on tumor size). (C) Representative maximum intensity projections illustrating intratumoral mock (Left) and h19m28z CAR T cells (Right) 28 d after i.v. injection. (Scale bars: 100 µm.) (D) Distance of intratumoral CAR T cells from brain surface (pooled data from 1 to 3 3D ROIs per mouse). Each point represents an individual mock or h19m28z CAR T cell. T cell number and position after tumor regression (day 28: 3 of 8 mice in the h19m28z group, 0 of 5 in the mock group) have been excluded. ***P < 0.001. (E and F) Intracerebral, 2D tumor area assessed by in vivo microscopy after mock and h19m28z CAR T cell treatment. Individual (E) and pooled (F) tumor size. (B–F) n = 5 and 8 for mock and h19m28z CAR T cell treatment, respectively, from 4 independent experiments. Data are shown as mean + SEM (B) or median (D). Mann–Whitney U test (B and D) or 2-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (F). ns, not significant.