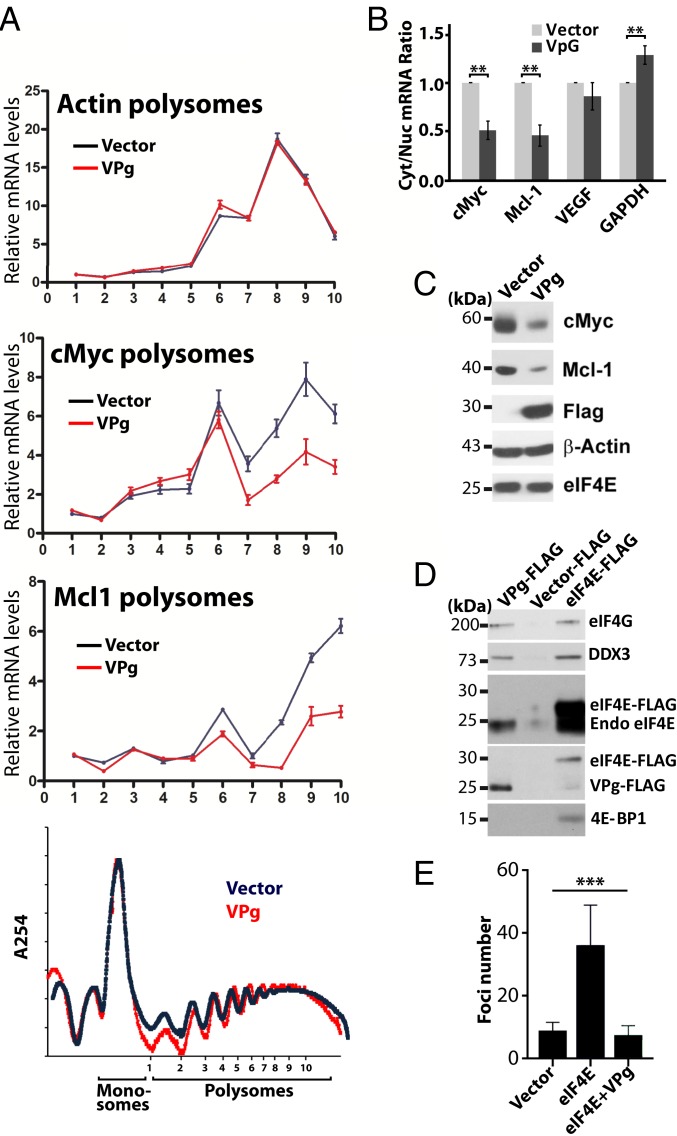
Fig. 6.
VPg represses eIF4E function in human cancer cells. (A) Polysome analyses of cells expressing VPg or vector controls indicates that VPg reduces translation efficiency of c-Myc and Mcl1 RNAs but not Actin, the negative control, without altering the global polysome profile (Lower). (B) VPg inhibited eIF4E-dependent mRNA export for targets RNAs. RNA levels were measured in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions by qRT-PCR. While the increase in GAPDH was significant, it was so modest that it seems unlikely to be physiologically relevant. P values are shown. (C) Western blot analysis of the effects of VPg overexpression on eIF4E targets Mcl1 and cMyc. VPg–FLAG levels are given, and actin is provided as a loading control. Note that VPg does not lower endogenous eIF4E protein levels. (D) FLAG immunoprecipitations from cells overexpressing VPg–FLAG, eIF4E–FLAG, or controls. Blots were probed as indicated. (E) VPg overexpression suppresses formation of foci in eIF4E–Myc overexpressing cells. ANOVA (P < 0.0009) was conducted. Experiments were carried out 3 independent times; means ± SDs are shown in A, B, and E (***P < 0.001).