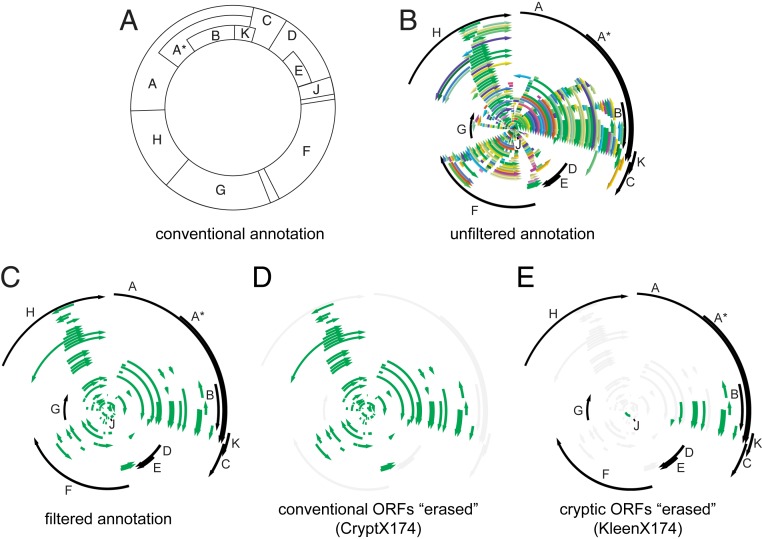
Fig. 1.
Designing genomes encoding only essential or only cryptic ORFs. (A) Contemporary genetic map of øX174. Lettered boxes represent the 11 established protein-coding ORFs. (B) The øX174 genome with 315 ORFs, each 60 bp or longer and starting with an ATG, GTG, or TTG codon (various colors), plus the 11 established protein-coding ORFs (black). (C) Filtered annotation of the øX174 genome with ORFs; 11 previously identified protein-coding ORFs (black) and 82 cryptic ORFs of unknown protein-coding status (green). (D) The cryptX174 genome design with the 11 established ORFs disrupted (gray), and 82 cryptic ORFs of unknown protein-coding status (green). (E) The kleenX174 genome design showing disruption of 71 cryptic ORFs (gray), 11 previously identified protein-coding ORFs (black), and remaining 11 cryptic ORFs of unknown protein-coding status (green).