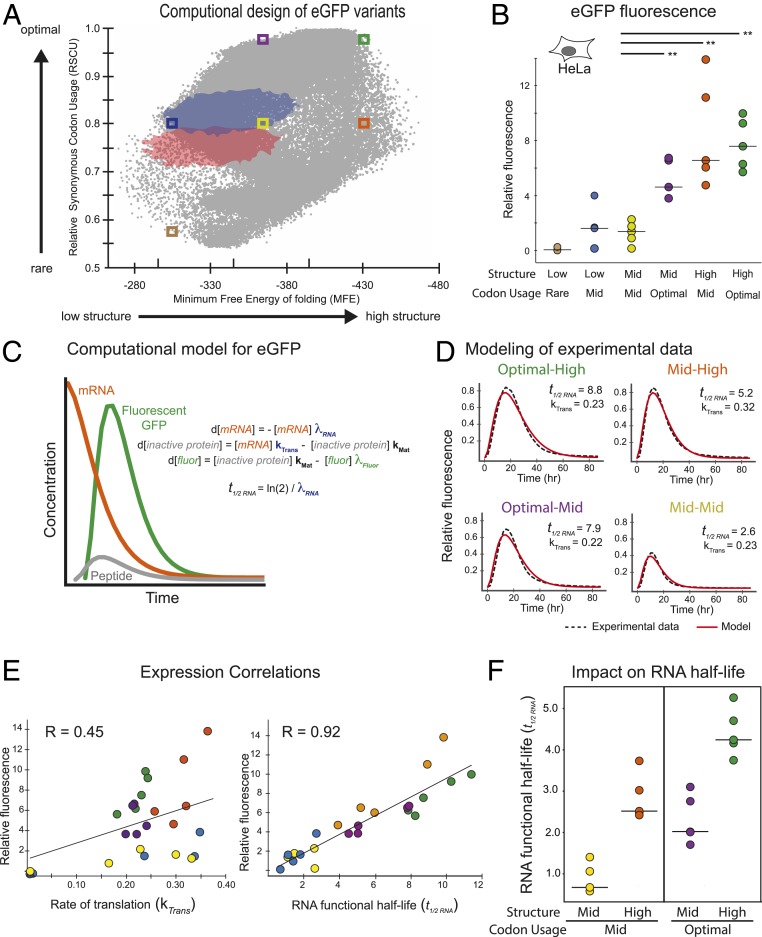
Fig. 5.
Half-life of computationally designed eGFP-degron mRNAs is determined by codon usage and mRNA structure. (A) Codon optimality (relative synonymous codon usage, y axis) versus secondary structure (energy of the predicted MFE structure, x axis) for sets of 150,000 generated eGFP sequence variants generated using codons chosen randomly (red), weighted in proportion to the human genome(blue), and using our algorithm (gray). Colored boxes show regions from which sequences were selected for further testing. (B) Total integrated eGFP fluorescence measured every 2 h for 86 h in HeLa cells (relative fluorescence unit [RFU], y axis) for 6 sets of 5 mRNAs containing m1Ψ (dots, with median as black line) with differing degrees of codon optimality and/or secondary structure (x axis, as in A). Significant differences by 2-way ANOVA comparisons are indicated by lines above, and P values are noted by asterisks (**P ≤ 0.01). (C) Model of eGFP expression kinetics. Simulated curves based on equations for changes in levels of mRNA (mRNA, orange), immature nonfluorescent protein (inactive protein, gray), and mature fluorescent protein (fluor, green) over time using exponential decay rates for mRNA (λRNA) and eGFP protein (λFluor), and rates of translation (kTrans) and protein maturation (kMAT). mRNA half-lives (t1/2 RNA) were calculated from the observed mRNA decay rates. (D) eGFP-degron fluorescence in HeLa cells (RFU, y axis) versus time (x axis) as measured experimentally (solid colored lines as in A) and fitted according to the model in C (dashed black lines) for representative sequence variants with differing degrees of codon optimality and/or secondary structure (as in A). Translation rate constants (kTrans) and mRNA half-lives (t1/2 RNA) as derived from the model described in C are shown. (E) Total eGFP-degron fluorescence in HeLa cells (RFU, y axis) versus the modeled rate constants for translation (kTrans, Left) or mRNA functional half-life (λRNA, Right) for 20 sequence variants containing m1Ψ as in D. Linear regression (black line) and Pearson correlation are shown. (F) Modeled functional mRNA half-lives (λRNA, y axis) for 4 sets of 5 eGFP-degron sequence variants with differing degrees of codon optimality and/or secondary structure (x axis, as in A and B).