Figure 1.
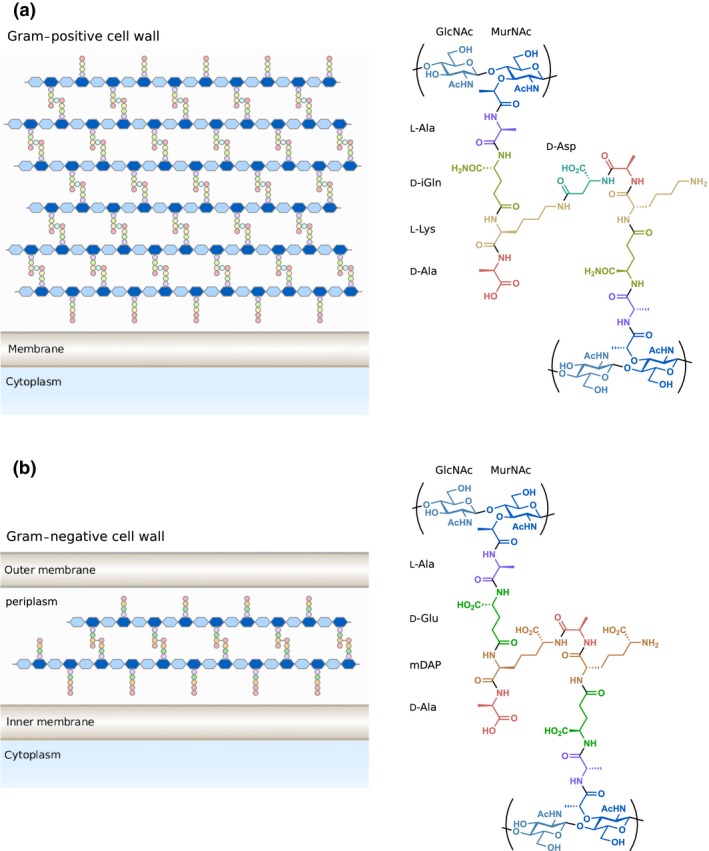
Structure of Gram‐positive and Gram‐negative peptidoglycan. (a) Gram‐positive bacteria like Enterococcus faecium contain a thick layer of peptidoglycan outside of their single membrane. Gram‐positive bacteria usually contain d‐isoglutamine (d‐iGln) and L‐lysine at the second and third positions of the peptide stem. (b) Gram‐negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli contain a thin layer of peptidoglycan within their periplasm. Gram‐negative bacteria generally utilise d‐glutamate (d‐Glu) and meso‐diaminopimelic acid (mDAP) at the second and third positions of the peptide stem. The location and composition of the crosslink between peptide stems vary between species. Ac, acetyl.
