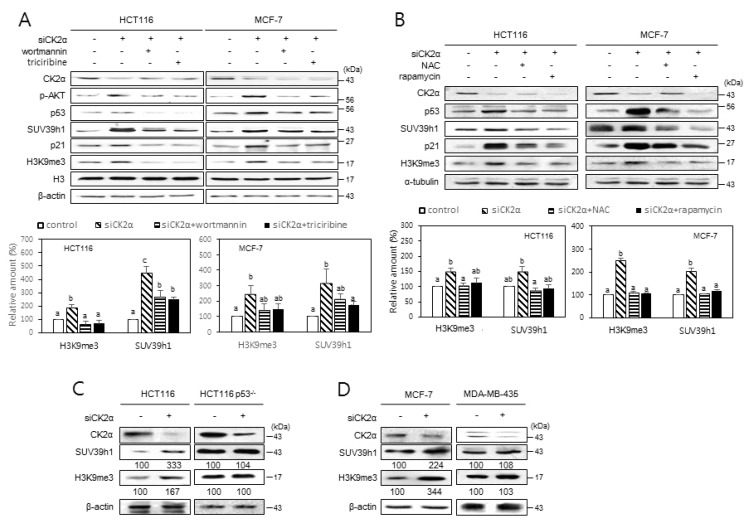
Fig. 1. Induction of H3K9me3 and SUV39h1 after CK2 downregulation requires PI3K-AKT-mTOR-ROS-p53 pathway.
(A and B) Cells were treated with CK2α siRNA for 48 h in the presence of 100 nM wortmannin or 10 μM triciribine (A) and 5 mM NAC or 100 nM rapamycin (B). Cell extracts were then visualized by immunoblotting (upper panels). Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. The graph shows the quantification of each protein relative to α-tubulin (A) or β-actin (B) (bottom panels). Values indicate mean ± SEM. Bars that do not share a common letter (a, b, or c) are significantly different between groups at P < 0.05. (C and D) Essential role of p53 in inducing H3K9me3 and SUV39h1 upon CK2 downregulation. Wild-type p53 cells (HCT116 and MCF-7) and mutant p53 cells (HCT116 p53−/− and MDA-MB-435) were treated with CK2α siRNA, and cell extracts were visualized by immunoblotting. The values below each band represent the mean fold differences (n = 3) in expression levels compared to the control, which was assigned a value of 100.