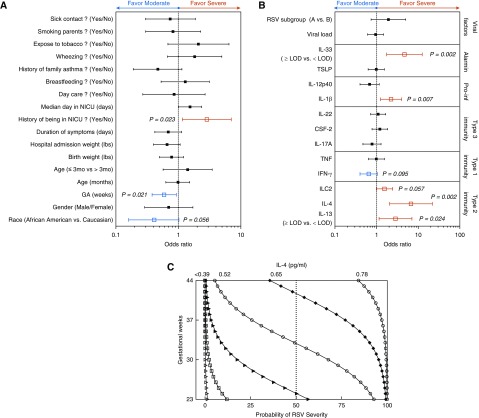
Figure 4.
Younger gestational age (GA) positively correlates with higher levels of IL-4 in response to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection and more severe disease. (A and B) Plots of risk factors for the development of severe RSV, using bivariate logistic regression of (A) background variables and (B) immune/host-related variables, with pediatric ICU admission status as the dependent variable. The vertical line represents an odds ratio of 1. Odds ratio with 95% confidence interval; P ≤ 0.05. (C) The combined influence of nasal aspirate levels of IL-4 and GA on the severity of RSV disease in infants was assessed using multivariable logistic regression. The logarithm of the odds Pr/(1 − Pr), where Pr is the probability of the disease severity, depends on a vector of predictors (IL-4 and GA), is logit(Pr) = log[Pr/(1 − Pr)] = β0 + βIL4 × IL4 + βGA × GA, where β is a vector of regression coefficients. In the final logistic regression model, β0 = −0.62, βIL4 (0.13 pg/ml) = 2.269, and βGA (2.76 wk) = −0.709. Duration of symptoms refers to duration of symptoms before sampling. ILC2 = innate lymphoid type 2 cell; LOD = limited of detection; NICU = neonatal ICU; Pro-inf = proinflammatory cytokines.