Fig. 1. Endochondral bone generation (reproduced from [1] with permission).
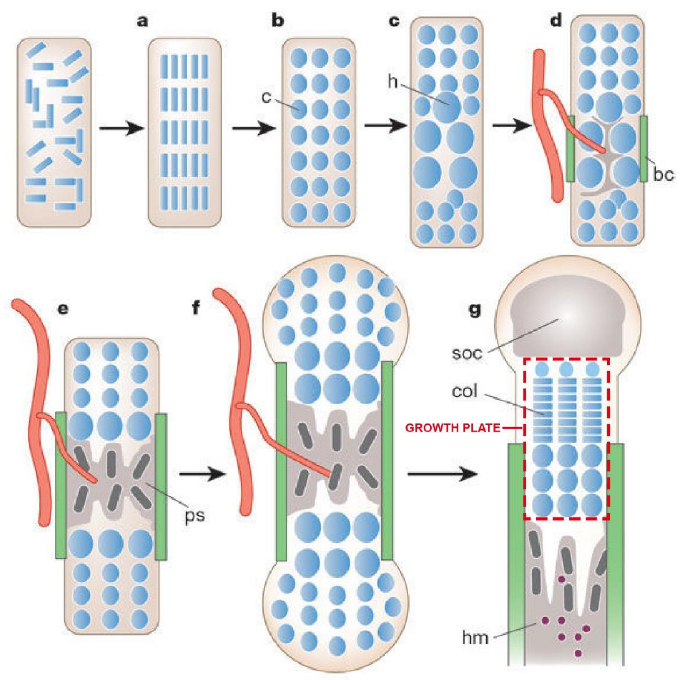
(a) Condensation of mesenchymal cells (blue). (b) Condensed cells developed into chondrocytes. (c) Hypertrophic chondrocytes are generated at the center of condensation. (d) Bone collar is formed, and hypertrophic chondrocytes induce mineralized extracellular matrix (ECM) and invasion of blood vessels. (e) Primary spongiosa is generated by osteoblasts. (f) Osteoblasts of bone collar and primary spongiosa become cortical bone and trabecular bone, respectively. (g) Secondary ossification center is formed at the end of bone and columns of chondrocytes are generated in the proliferation zone of growth plate. Haematopoietic marrow is generated in bone marrow space. c: chondrocytes, h: hypertrophic chondrocytes, bc: bone collar, ps: primary spongiosa, soc: secondary ossification center, col: columns of proliferating chondrocytes, hm: Haematopoietic marrow.
