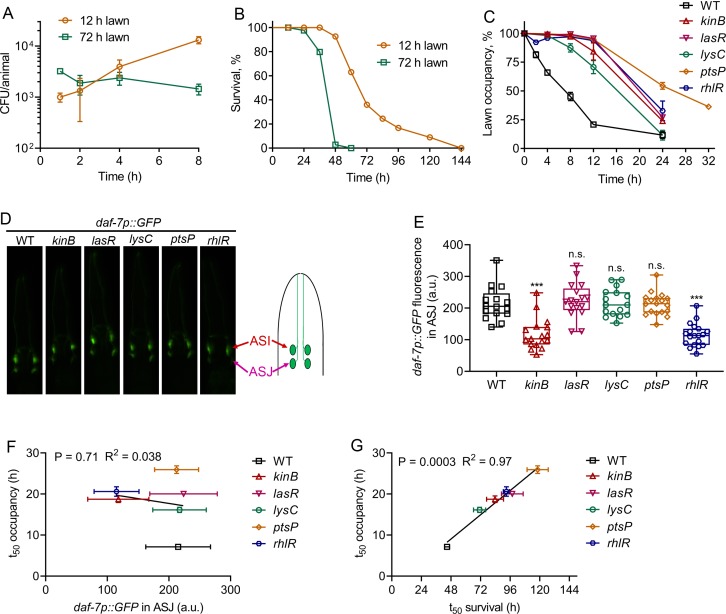
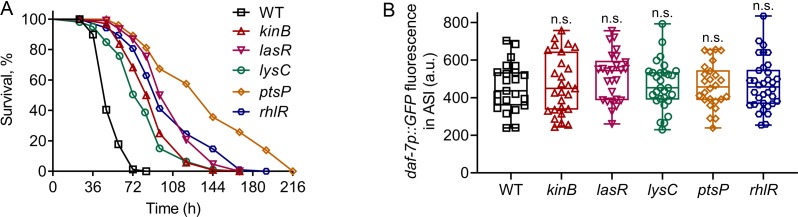
Figure 4. P. aeruginosa virulence correlates with the avoidance behavior.
(A) Time course of colony-forming units (CFU) per animal of N2 animals exposed to 12 and 72 hr lawns of P. aeruginosa-GFP. (B) Representative survival plots of N2 animals on 12 and 72 hr lawns of P. aeruginosa. p<0.0001. (C) Time course of the percent occupancy of N2 animals on 72 hr lawns of different mutants of P. aeruginosa. (D) Representative photomicrographs of daf-7p::GFP expressing animals exposed for 4 hr to lawns of different mutants of P. aeruginosa. The drawing depicts the arrangement of the ASI and ASJ neurons in C. elegans head. (E) Quantification of daf-7p::GFP in the ASJ chemosensory neuron pair in animals exposed for 4 hr to lawns of different mutants of P. aeruginosa. ***p<0.001 via the t test. n.s., non-significant. (F) Correlation of the mean lawn occupancy time (t50 occupancy) to the corresponding levels of daf-7p::GFP in the ASJ chemosensory neuron pair in animals exposed to different P. aeruginosa mutants. (G) Correlation of the mean lawn occupancy time (t50 occupancy) to the corresponding mean survival time (t50 survival) in animals exposed to different P. aeruginosa mutants.