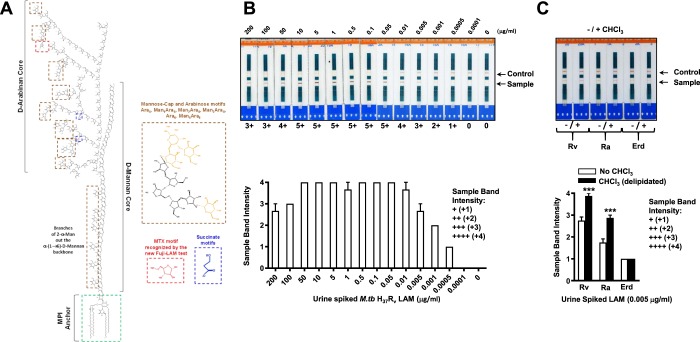
Figure 1.
(A) Structure of mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan (ManLAM) present in all M.tb complex strains. ManLAM (depicted here as LAM) is a heterogeneous molecule comprised of a GPI-anchor, which can contain from 1–4 fatty acids, an α-(1 → 6) mannan core with multiple branches of a single mannose, an α-(1 → 5) arabinan core with multiple branches of different length at the C3 position of some arabinoses. The non-reducing end of some of these arabinan branches are decorated with 2-α-mono-, di- and tri-mannosaccharide caps. A 5-methyl-thio-xylose (MTX) is present per LAM molecule, being the epitope recognized by the new FujiLAM test. LAM also contains succinate motifs, which biological function is still unclear but participate in determining the spatial conformation of LAM. (B) Alere Determine LAM Ag test (LAM-test) performed in M.tb H37Rv LAM spiked urine determining that the lowest amount that this test can detect LAM in urine is 0.0005 μg/ml of urine (500 pg). (C) A quick delipidation step for LAM spiked urine using chloroform (CHCl3) improves the detection of LAM by the LAM-test. Student’s t test, treatment vs. non-treatment, n = 3–8, using LAM spiked urine from different human donors; ***p < 0.0005.