Fig. 2.
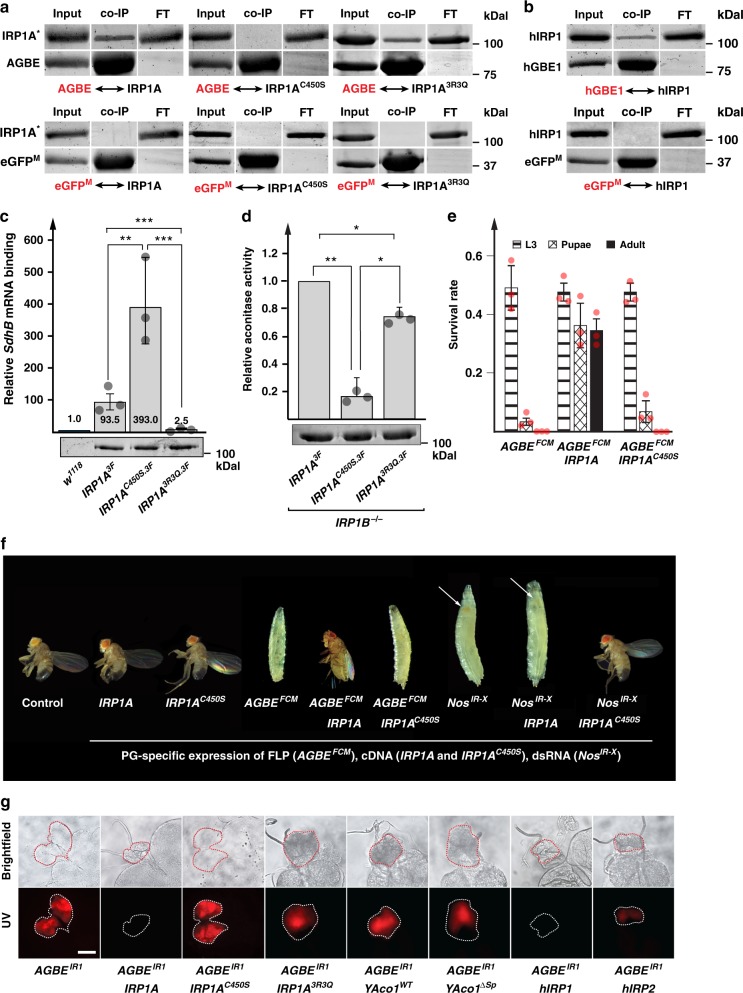
AGBE interacts with IRP1A. a Co-transfection of S2 cells with plasmids encoding Flag-tagged IRP1A variants (IRP1A*) and Myc-tagged AGBE followed by immunoprecipitation via anti-Myc antibodies and Western blotting. Names shown in red indicate the protein used as bait. IRP1A: wild type IRP1A, IRP1AC450S: constitutively RNA-binding IRP1A, IRP1A3R3Q: non-RNA-binding form of IRP1A (Supplementary Table 1). Myc-tagged enhanced GFP (eGFPM) served as a negative control. Input lane represents 10% of the sample. Presence of co-immunoprecipitated proteins were tested with anti-Flag antibodies. b Like A, but co-transfection of S2 cells with plasmids encoding Flag-tagged human IRP1 (aka Aco1) and Myc-tagged human GBE1, as well as eGFPM as a negative control. c Quantitative RNA-immunoprecipitation (RIP). Samples from larvae carrying Flag-tagged knock-in alleles of IRP1A (IRP1A3F, IRP1AC450S.3F, and IRP1A3R3Q.3F) (Supplementary Fig. 4) were normalized via Western blotting to visualize Flag-tagged proteins followed by ImageJ quantification. Western blot of adjusted samples shown below graph. Untagged IRP1A (control line w1118) served as a negative control and calibrator (normalized expression = 1). SdhB mRNA harbours a validated IRE72,73. Co-immunoprecipitated SdhB mRNA was quantified via qPCR. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals from three biological replicates. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. d Aconitase activity. Same IRP1A alleles and normalization procedure as described in c, except that IRP1A3F served as the control (normalized to 1). All alleles were crossed into an IRP1B−/− mutant background to eliminate the aconitase activity of IRP1B. Further, we removed mitochondria via ultracentrifugation to reduce the contribution of mitochondrial aconitase. Error bars represent standard deviation from three biological replicates. ** p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. e Survival rates of PG > FLP; AGBEFCM animals (Supplementary Fig. 4), which causes Flippase-mediated excision of the AGBE transcription unit specifically in the prothoracic gland (PG). Tested in either the presence or absence of the IRP1A and IRP1AC450S transgenes that are also expressed in a PG-specific manner. Error bars represent standard deviation from three biological replicates (each sample contained 50 individuals). f Larval and adult phenotypes of PG > FLP; AGBEFCM and PG > NosIR-X animals expressing IRP1AC450S or wild type IRP1A transgenes. Arrows point to red-stained PG. g Ring glands dissected from PG > AGBEIR1 larvae in the presence or absence of the following transgenic cDNAs: IRP1A (wild type IRP1A); IRP1AC450S (constitutively RNA-binding); IRP1A3R3Q (non-RNA-binding); YAco1WT: wild type yeast aconitase (mitochondrial); YAco1∆Sp (cytoplasmic); hIRP1 & hIRP2: human IRP1 & IRP2. Scale bar = 250 μm. All transgenes are expressed in a PG-specific manner via the Gal4-UAS system. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.