Fig. 1.
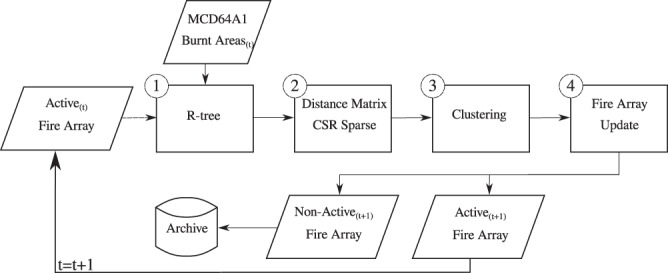
Diagram depicting the data mining process for each execution step. The first step is the creation of an R-tree with those fires that are considered active. Using the R-tree with the new burnt areas from MCD64A1 in vector format a distance sparse matrix compressed by rows is created considering the minimum distance between geometries and time stamps. Next, the compressed sparse matrix by rows is used as input for the DBSCAN, which will return the labels for the clusters. Finally, the fire array is updated with the labels, and those fires which are no longer considered as active are archived.
