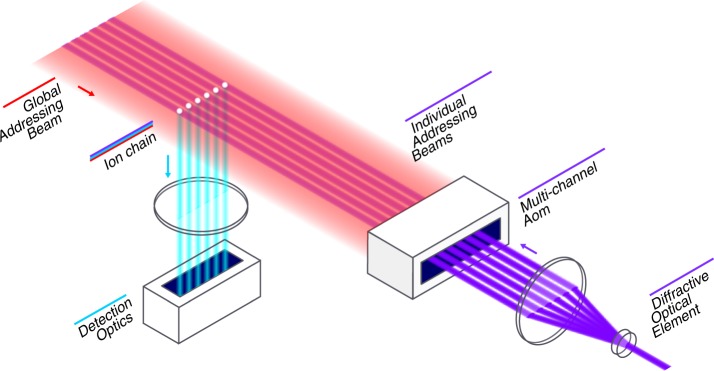
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the hardware. A linear chain of ions is trapped near a surface electrode trap (trap is not shown). Lasers at 369 and 935 nm (not shown) illuminate all of the ions during cooling, initialization, and detection. Each ion’s fluorescence is imaged through a 0.6 numeric aperture lens (detection optics) and directed onto individual photomultiplier tube channels. Two linearly polarized counterpropagating 355 nm Raman beams are aligned to each qubit-ion, a globally addressing beam that couples to all of the qubits (red) and an individual addressing beam that is focused onto each ion (blue). Acousto-optic modulators (AOMs) modulate the frequency and amplitude of each of these beams to generate single-qubit rotations and XX-gates between arbitrary pairs of qubit ions.