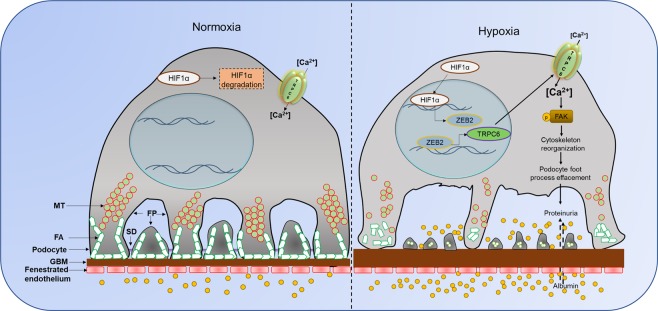
Figure 8.
Proposed model for ischemic-hypoxia mediated podocyte injury. Ischemia-stroke rats develop systemic hypoxia that induces HIF1α accumulation in several susceptible sites including glomerular podocytes. HIF1α drives ZEB2 expression, which in turn induces TRPC6 expression. Elevated TRPC6 increases intracellular calcium levels and calcium-dependent phosphorylation of FAK elicits cytoskeletal rearrangements. These cytoskeletal rearrangements eventually manifest in the effacement of podocyte foot-processes and increased permeability to proteins and large molecules. The overactivity of the HIF1α/ZEB2/TRPC6 axis in podocytes elicits cytoskeletal abnormalities and proteinuria.