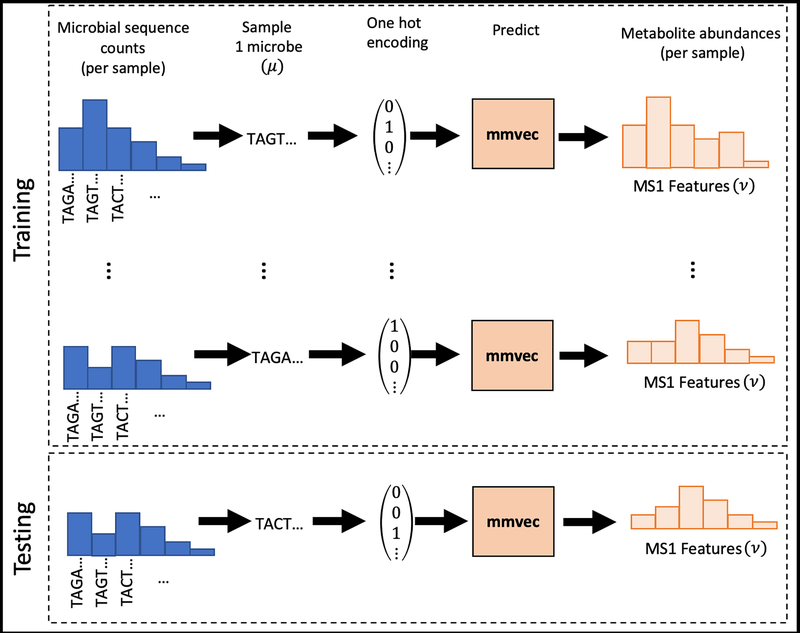
Figure 1:
Input data types and mmvec neural network architecture. (a) The neural network architecture where the input layer represents one-hot encodings of N microbes and the output layer represents the proportions of M metabolites. U corresponds to microbial vectors and V corresponds to metabolite vectors. (b) The pipeline for training mmvec. The objective behind mmvec is to predict metabolite abundances (y) given a single input microbe sequence (x), also known as a one-hot encoding. This training procedure will estimate conditional probabilities of observing a metabolite given the input microbe sequence. Cross-validation can be performed on hold-out samples to access overfitting.