Figure 5:
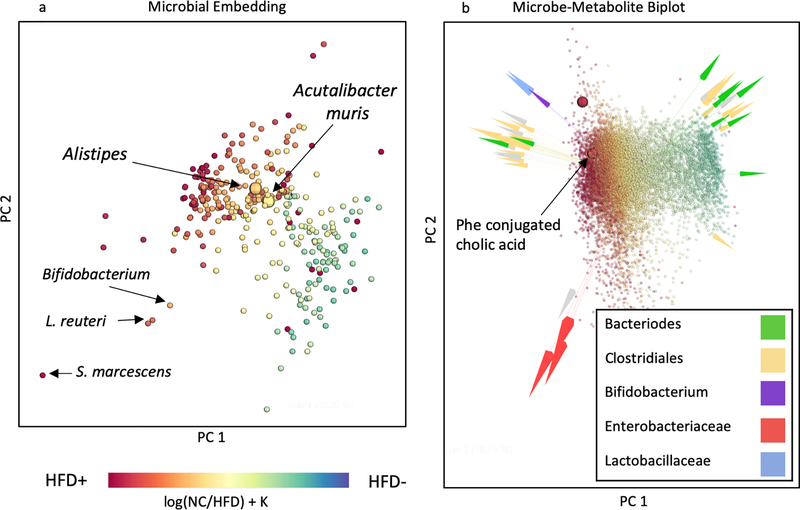
Microbe/metabolite co-occurrences across study of HCC progression in the context of innate immunity in a mouse model [28]. (a) Visualization of microbial co-occurrence patterns, where distances between points approximates the Aitchison distance between microbes, which quantities microbial occurrences. Small distances are indicative of microbes with high probability of co-occurring together. Microbes are colored according to their association with HFD, which was estimated using differential abundance analysis via multinomial regression. (b) Emperor [59] biplot of microbe-metabolite interactions, with metabolites colored according to their association with HFD. HFD association was estimated through differential abundance analysis via multinomial regression. Distances between points approximate Aitchison distances between metabolites and distances between arrow tips approximate Aitchison distances between microbes. Several Clostridium spp. appear to co-occur with the new bile acid molecule cholate phenylalanine amidate, also referred to as Phe conjugated cholic acid.