Figure 2.
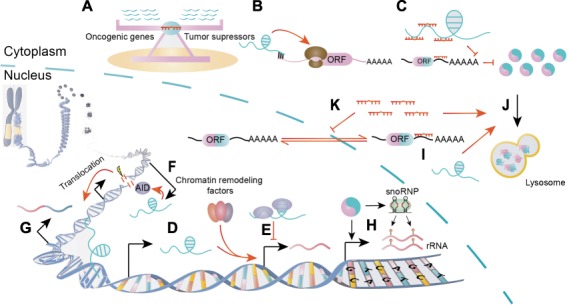
The various modes of actions of ncRNAs in fusion protein-driven cancers. (A) The miRNAs function in a teeterboard manner. (B–E) The lncRNAs play their roles by regulating translation (B), competing for miRNA binding (C), recruiting chromatin-remodeling complex (D), and binding proteins to regulate gene expressions (E). (F and G) The lncRNAs possibly facilitate AID-dependent gene translocation by transcription opposite to the sense strands (F) or bring two translocation partners into close proximity by directing interacting with their DNA loci (G). (H) Fusion proteins deregulate snoRNA and/or rRNA to exert procancer functions. (I–K) The ncRNAs can directly target fusion transcripts (I), regulate fusion protein degradation (J), or the nucleoplasmic transport of fusion mRNA pathways (K).
