Figure 3.
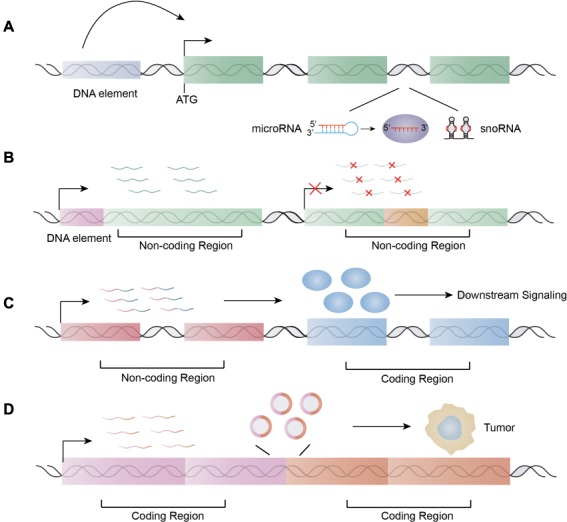
ncRNAs are directly involved in chromosome translocation. (A) ncRNA-convergent fusions. (B) The chromosomal translocation sites reside in the ncRNA regions: production of new ncRNAs by juxtaposition of regulatory elements upstream of non-coding regions or disruption of original ncRNA. (C) The fusions of non-coding regions with coding regions lead to the dysregulations of coding products and subsequent alterations of related signaling pathways. (D) The coding fusion transcripts or the derived non-coding isoforms, such as circRNAs by back-splicing, function as regulatory RNAs.
