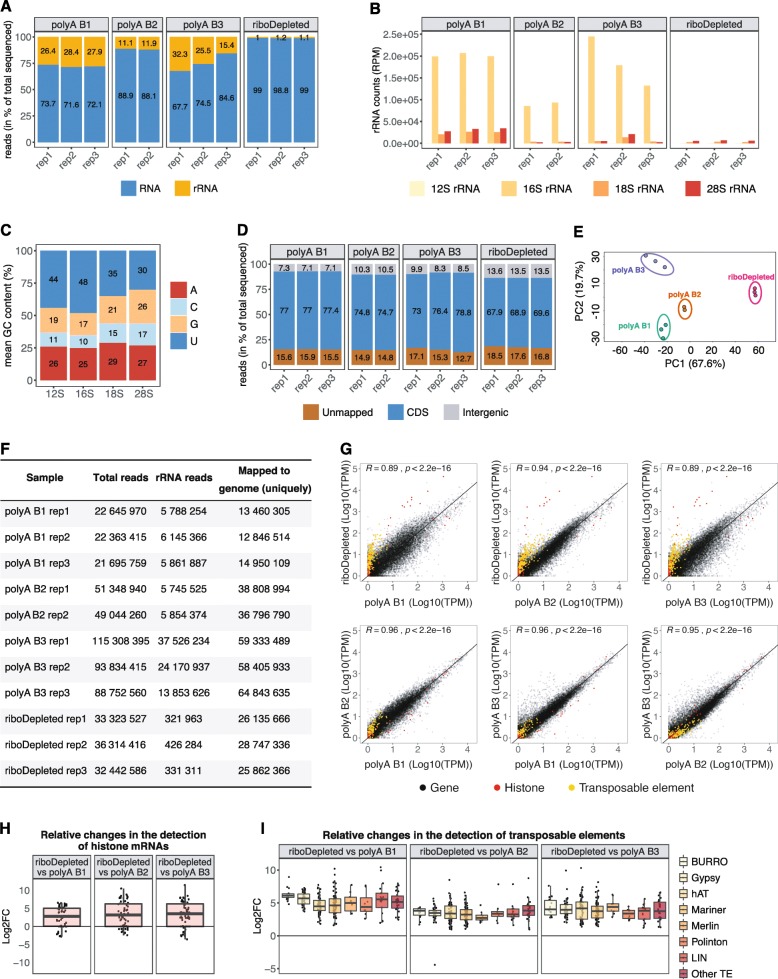
Fig. 3.
Comparison of rRNA-depleted and poly(A)-enriched planarian RNA-seq libraries. a Percentage of rRNAs reads in the sequenced libraries prepared from rRNA-depleted or poly(A)-enriched RNA. b rRNAs species remaining in the final sequenced libraries. c Nucleotide content of planarian rRNA. d Percentage of sequenced reads mapped to coding (CDS) and intergenic regions in the planarian genome. e Principal component analysis (PCA) biplot of log2 expression data for coding genes reveals distinct clustering of all analyzed RNA-seq experiments. f Sequencing depth and number of reads mapped to the planarian genome in analyzed ribodepleted and poly(A)-enriched samples. g Comparison of gene expression in transcripts per million (TPM) between planarian ribodepleted and poly(A)-enriched (polyA) RNA-Seq data. The Pearson’s correlation coefficient is indicated. h Increased representation of histone mRNAs in ribodepleted libraries. i Boxplot of log2 fold changes in the expression values of transposable elements between ribodepleted and poly(A)-enriched libraries