Figure 2. Insights from an atomic resolution cryoEM structure of Yme1,
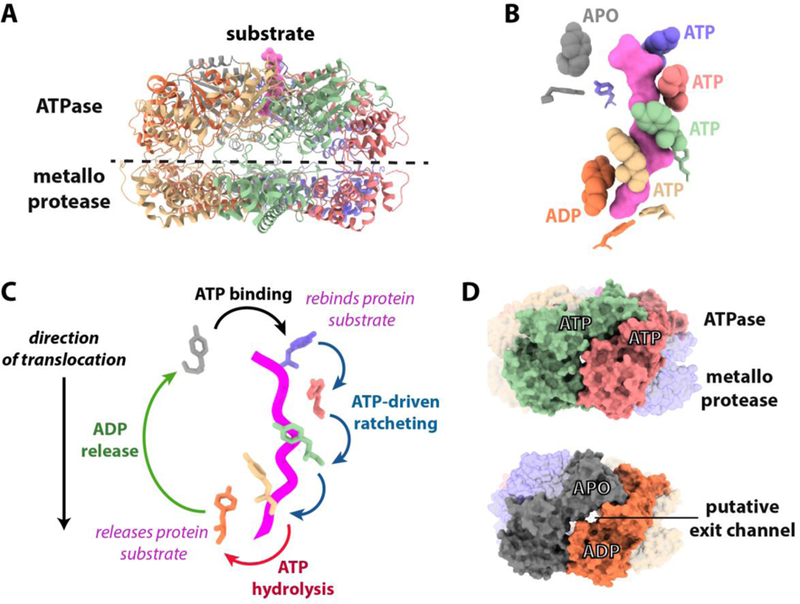
(A) Ribbon model showing the cryoEM structure of the hexameric Yme1 catalytic core[31]. Substrate polypeptide trapped in the ATPase spiral is colored pink. (B) The translocating pore loops surround the substrate in a spiral staircase. The side chains of the substrate-contacting pore loop 1 and pore loop 2 tyrosine residues are shown as balls and sticks, respectively. (C) How cycling of pore loop positions driven by sequential ATP hydrolysis can drive hand-over-hand translocation. Suggested transitions between the positions of pore-loop 1 tyrosines during the ATP hydrolysis cycle are shown based on the hexameric Yme1 structure. The coloring of the tyrosines matches that from 2B and substrate polypeptide is shown as a pink worm. (D) Putative exit channels appear dependent on subunit nucleotide state. Surface representations of Yme1 showing the appearance of lateral channels ~3.5 Å in diameter between apo and ADP bound subunits that are not seen between ATP bound subunits. Channel dimensions were calculated using Caver 3.0[77].
