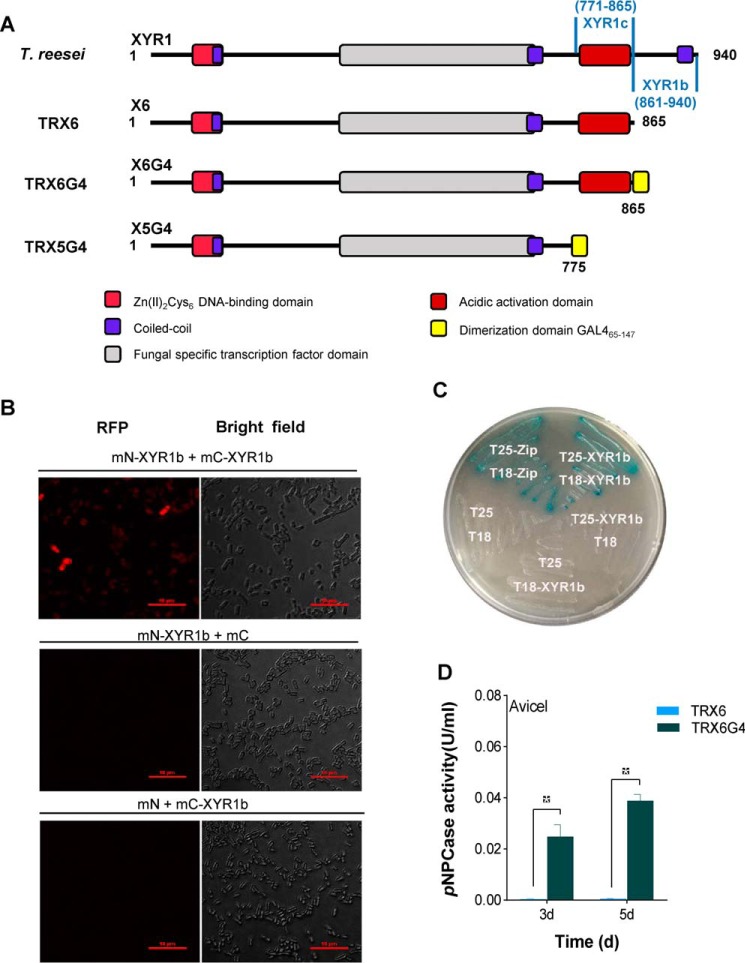
Figure 4.
C-terminal domain of XYR1 mediates homodimerization. A, construction of T. reesei TRX6G4 and TRX5G4. The XYR1b domain is amino acids 861–940 of XYR1; the XYR1c domain is amino acids 771–865 of XYR1; and GAL465–147 is a well-known dimerization domain of GAL4 (amino acids 65–147) from S. cerevisiae. The structure of XYR1 is from Lichius et al. (24). B, BiFC assay showing the protein–protein interactions in the XYR1b domain in E. coli. Strains expressing protein partners fused with N-terminal aa 1–159 of a fluorescent protein mCherry (mN) or C-terminal aa 160–237 of mCherry (mC) are indicated on each panel. Negative controls for the BiFC assay of the XYR1b domain were performed (mN-XYR1b + XYR1b and mN + mC-XYR1b). Positive interactions resulted in red fluorescence. C, B2H assay reveals the protein–protein interactions of the XYR1b domain. Strains with proteins that could bind with each other showed up as a blue colony on M63 plates supplemented with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl β-d-galactoside and isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside. T18 and T25 are two complementary fragments of adenylate cyclase (CyaA), obtained from Bordetella pertussis. Zip, the leucine zipper motif of GCN4. Strains are indicated by their expressed T18 or T25 fusion proteins. A strain expressing T25-zip and T18-zip fusion proteins was used as a positive control. It was observed as a blue colony (Cya+ phenotype) because of the dimerization of leucine zipper motifs, which were appended to the T25 and T18 fragments, respectively. A strain expressing T18 and T25 was used as the negative control. The strain expressing T25-XYR1b and T18-XYR1b fusion proteins was observed as a blue colony, which indicates a positive protein–protein interaction. D, pNPCase activities of T. reesei strains TRX6G4 and TRX6 on Avicel.