Figure 6.
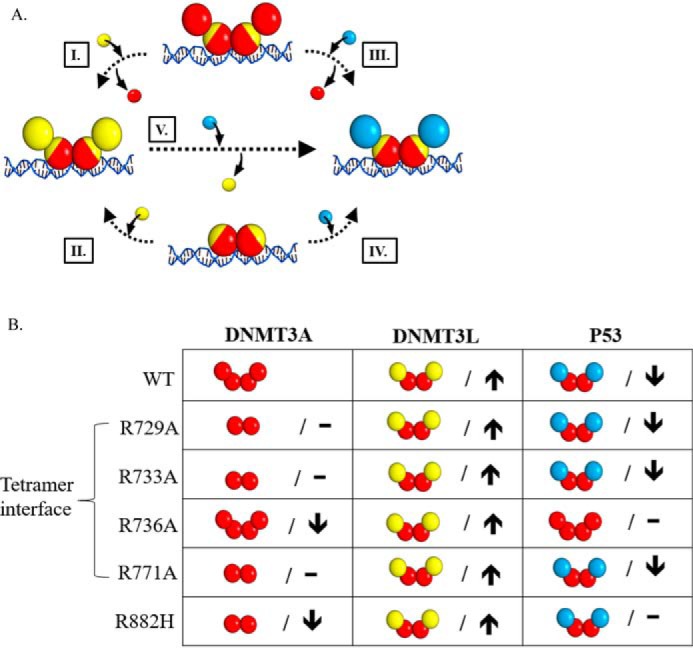
Mutations in DNMT3A lead to diverse interactions with p53. A, the addition of DNMT3L (yellow square) to DNMT3A homotetramers or homodimers (red square tetramer interface depicted in yellow) leads to the formation of DNMT3A (red square)-DNMT3L (yellow square) heterotetramers (I and II). Similarly, p53 (blue square) interacts with DNMT3A homotetramers or homodimers (red square) to form DNMT3A (red square)-p53 (blue square) heterotetramers (III and IV). Furthermore, the addition of p53 (blue square) to DNMT3A (red square)-DNMT3L (yellow square) heterotetramers displaces monomers at the tetramer interface and leads to the formation of DNMT3A-P53 (blue square) heterotetramers (V). B, summary of the oligomeric states of DNMT3A mutants in complex with DNMT3L (28, 36) and p53 as well as the effects on the catalytic function of DNMT3A. DNMT3A mutants display no change (–) or decreased (↓) activity (kcat) relative to WT. Although all the DNMT3A mutants are responsive to DNMT3L stimulation (↑), DNMT3A mutants display varying p53 inhibition (↓). Although DNMT3A R736A and R882H are unresponsive to p53 inhibition (–), p53 binds R882H to form heterotetramer.
