Figure 8.
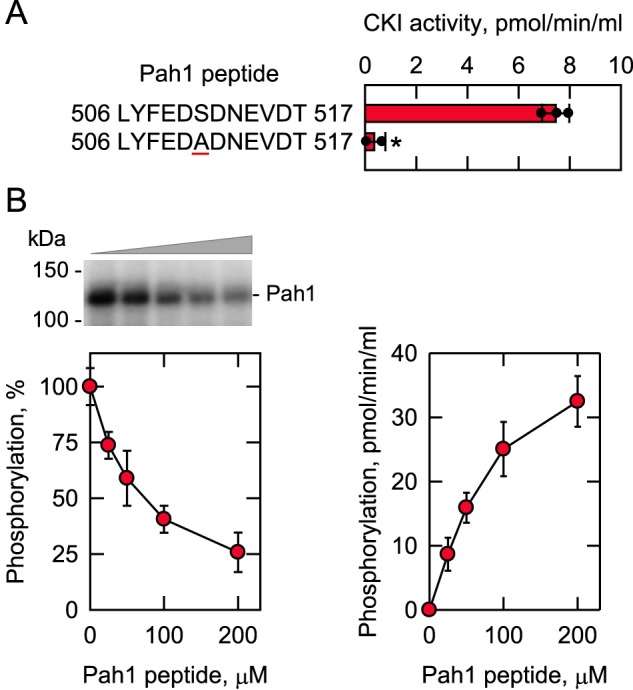
CKI phosphorylates the Pah1 synthetic peptide containing Ser-511; the synthetic peptide inhibits the phosphorylation of Pah1 by CKI. A, CKI activity was measured for 30 min with 100 μm of the indicated Pah1 synthetic peptides with 100 μm [γ-32P]ATP (5,000 cpm/pmol). The enzyme reaction was terminated by spotting the mixture onto P81 phosphocellulose paper, which was then washed with 75 mm phosphoric acid and subjected to scintillation counting. The numbers at the beginning and end of the peptides represent the positions in the full-length sequence of Pah1. The underlined residue within the peptide designates the serine–to–alanine substitution at position 511 in the sequence. The individual data points are also shown. B, Pah1 (1.25 μg/ml) was incubated for 30 min with 5 fmol/min CKI and 100 μm [γ-32P]ATP (5,000 cpm/pmol) in the absence and presence of the indicated concentrations of the WT Pah1 synthetic peptide. Following the CKI phosphorylation reaction, half of the sample was analyzed for the phosphorylation of Pah1 (left), and the other half was analyzed for the phosphorylation of the Pah1 peptide (right). Pah1 was separated from labeled ATP by SDS-PAGE and subjected to phosphorimaging and ImageQuant analysis. The extent of phosphorylation of the WT enzyme was set at 100%. The positions of Pah1 and the molecular mass standards are indicated. The phosphorylation of the Pah1 peptide was analyzed as described above. The data are the averages of three experiments ± S.D. (error bars). *, p < 0.05 versus WT. The phosphorimage shown in B (left) is representative of three experiments.
