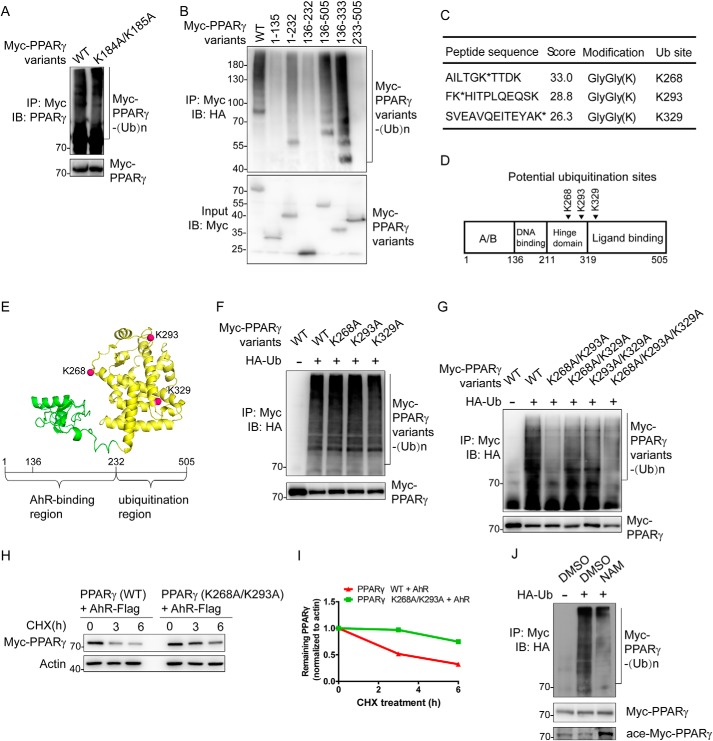
Figure 5.
Identification of ubiquitination site(s) in PPARγ. A, CRL4BAhR targets PPARγ for ubiquitination at a novel site(s). HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-Cul4B, AhR-Flag-His, HA-Ub, and Myc-PPARγ variants. Cells were treated with MG132 for 3 h and harvested for the following immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. Input (5%) was used for Western blotting. B, domain–domain interactions are required for PPARγ ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-Cul4B, AhR-Flag-His, HA-Ub, and Myc-PPARγ truncations. Cells were treated with MG132 for 6 h and harvested for the following immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. Input (5%) was used for Western blotting. C, list of PPARγ ubiquitination sites determined by MS. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-Cul4B, AhR-Flag-His, HA-Ub, and Myc-PPARγ. Cells were treated with MG132 for 10 h and harvested for immunoprecipitation using anti-Myc antibody. D, schematic structure of PPARγ. Arrowheads indicate potential ubiquitinated sites. E, the model of PPARγ isoform 2 (created from Protein Data Bank code 1PRG (65)) is demonstrated in cartoon. The AhR-binding region is colored green, and the ubiquitination region is colored yellow. Potential ubiquitination sites are shown as red spheres. F, single mutations on PPARγ barely affect ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-Cul4B, AhR-Flag-His, HA-Ub, and Myc-PPARγ variants. Cells were treated with MG132 for 3 h and harvested for the following immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. Input (5%) was used for Western blotting. G, effect of dual mutations on PPARγ ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-Cul4B, AhR-Flag-His, HA-Ub, and Myc-PPARγ variants. Cells were treated with MG132 for 3 h and harvested for the following immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. Input (5%) was used for Western blotting. H, effect of dual mutations on PPARγ stability. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids expressing AhR-Flag-His and Myc-PPARγ variants for CHX-chase assay. The final concentration of CHX used in the treatment was 60 μg/ml. The cell lysate was then detected with the indicated antibodies. I, turnover of WT and mutated PPARγ was determined by Western blotting. Signals from immunoblots were analyzed using Quantity One software. Protein signals of PPARγ variants were normalized with the actin protein signals, and the percentage of PPARγ variants remaining was plotted against time. J, SirT1 inhibitor NAM reduced PPARγ ubiquitination level. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-Cul4B, AhR-Flag-His, HA-Ub, and Myc-PPARγ. Cells were treated with MG132 (20 μm; 1.5 h) in the absence or presence of NAM (100 μm; 48 h). Cells were then harvested for the following immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. Input (5%) was used for Western blotting. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting.