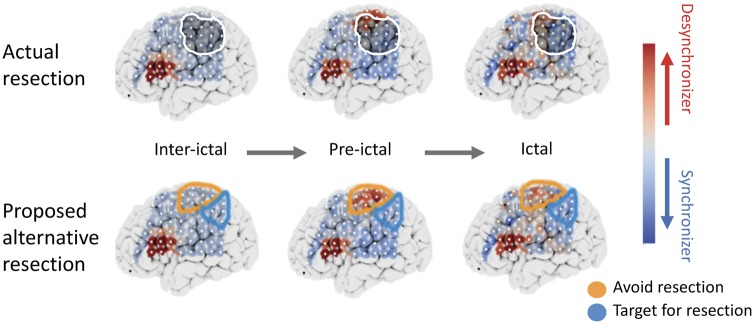
Figure 7.
Proposed framework for optimal resection targets using virtual resection. Median node-level control centralities during interictal, pre-ictal and ictal periods are shown for a sample patient who had poor outcome. The top row shows spatial maps with the resection zone (darkened region with white outline) and the bottom row shows regions that perhaps should be targeted for resection due to the presence of strong synchronizing nodes (blue), or should be avoided during resection because of the presence of strong desynchronizing nodes (red). Future experiments assessing the effects of stimulation of these nodes and subsequent changes in synchronizability will allow clinicians to better predict the effect of targeted resection of these nodes.