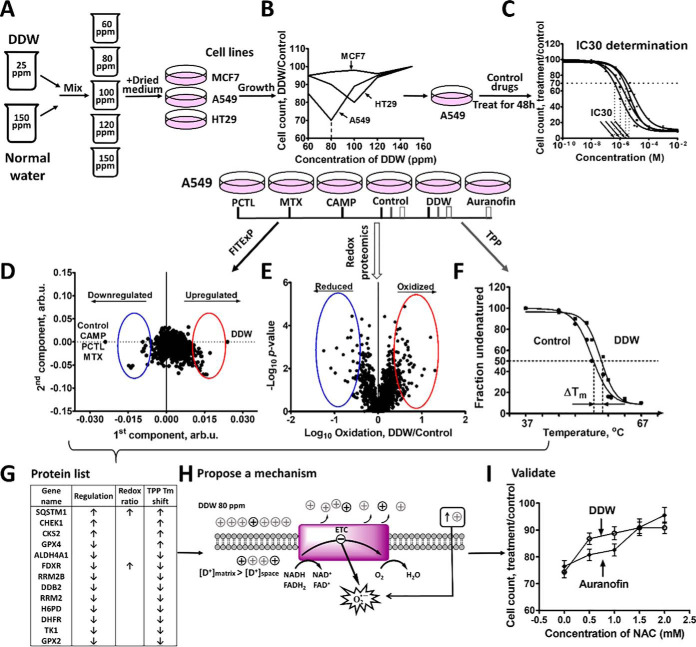
Fig. 1.
The layout of the proteomics-based characterization of DDW anticancer mechanism. A, DDW with varying deuterium concentration was prepared by mixing NW (150 ppm D) and 25 ppm DDW in different proportions. MCF 7, A549 and HT29 cells were grown in a DDW medium. B, Measurement of the cell lines responses to DDW. C, Determination of the concentrations of control drugs that inhibit cell growth by 30 ± 5% (IC30). D, Identification by FITExP analysis of the most regulated by DDW proteins compared with control drugs and NW. E, Measurement by redox proteomics of oxidation-reduction disbalance caused by DDW compared with NW control and auranofin. F, Measurement by TPP of proteome stability changes caused by DDW. G, Summary of the proteomics results reveals proteins mostly likely involved in DDW action. Proposing a DDW action mechanism (H) and its validation by additional experiments (I).