Fig. 5.
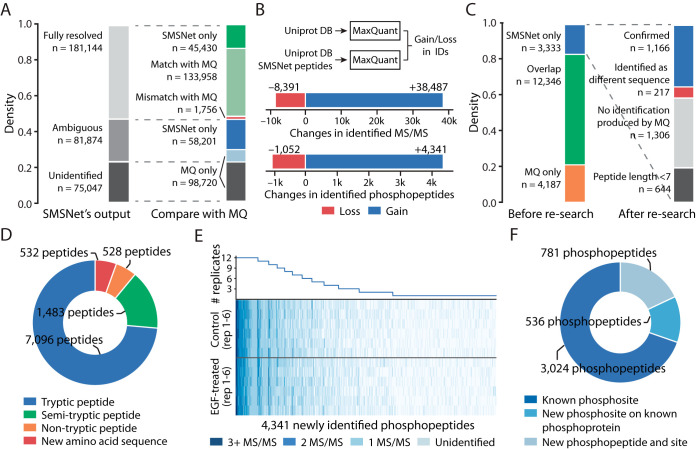
SMSNet improves the coverage of human phosphoproteome. A, Stacked bar plots showing the numbers of MS/MS spectra identified by SMSNet and the overlaps between SMSNet and prior study (18). B, The gains and losses in number of identified MS/MS spectra and phosphopeptides after adding SMSNet's identifications to the human proteome database and re-analyzing with MaxQuant (see Experimental Procedures). C, Stacked bar plots showing the numbers of phosphopeptides identified by MaxQuant and SMSNet and the numbers of new phosphopeptides that could be confirmed by re-analyzing SMSNet's identifications with MaxQuant. Peptides shorter than 7 amino acids were not considered during the search. “No identification produced by MQ” indicates that none of the MS/MS spectra of a phosphopeptide were identified as peptides by MaxQuant. “Identified as different sequence” indicates that none of the MS/MS spectra of a phosphopeptide were confirmed by MaxQuant as the same identification produced by SMSNet and at least one MS/MS spectrum was identified as a different peptide. D, Pie chart showing the composition of all newly identified peptides gained by adding SMSNet's identifications to MaxQuant's search. This includes phosphopeptide and non-phosphopeptide identifications from all MS/MS spectra that were not previously identified by prior study. It should be noted that because MaxQuant searches were performed with full-tryptic enzyme specificity, all identifications of semi-tryptic peptides, non-tryptic peptides, and peptides with new amino acid sequences were possible because of sequences supplied by SMSNet. E, Heatmap and line plot showing the reproducibility of 4,341 newly identified phosphopeptides after re-analysis using MaxQuant across 6 control and 6 epidermal growth factor (EGF)-treated replicates. Each row in the heatmap corresponds to one mass spectrometry experiment. F, Pie chart showing the overlap between newly identified phosphopeptides and known phosphoproteins and phosphosites in the PhosphoSitePlus database. An identified phosphopeptide was counted as “Known phosphosites” only if all identified phosphorylation sites on that peptide are reported in the database. Identified phosphopeptides that contain unreported phosphosites were grouped based on whether they could be mapped to known phosphoproteins in the database.