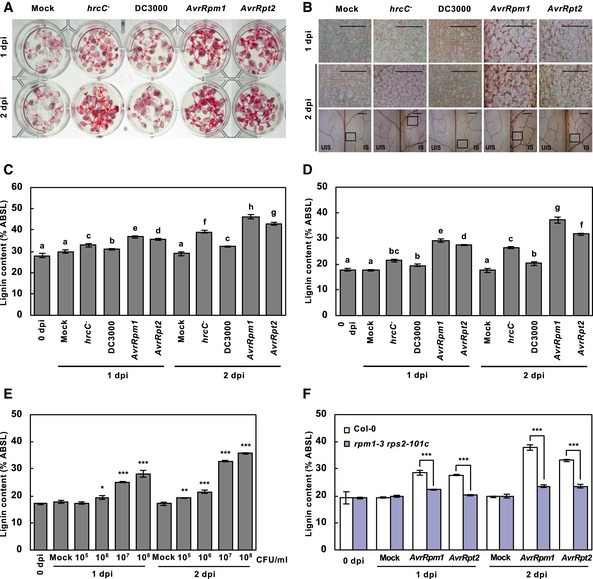
Phloroglucinol staining of wild‐type seedlings inoculated with PTI‐inducing Pst DC3000 hrcC
−
, virulent Pst DC3000, and avirulent Pst DC3000 (AvrRpm1) and Pst DC3000 (AvrRpt2).
Phloroglucinol staining of wild‐type adult leaves inoculated with PTI‐inducing Pst DC3000 hrcC
−
, virulent Pst DC3000, and avirulent Pst DC3000 (AvrRpm1) and Pst DC3000 (AvrRpt2). The upper images are enlarged ones of the lower boxes at 2 dpi. Scale bars, 100 μm.
Quantification of lignin content in pathogen‐treated seedlings as in (A). Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 4; 20–30 seedlings each).
Quantification of lignin content in pathogen‐treated wild‐type leaves as in (B). Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 4; 3–9 leaves each).
Quantification of lignin content in wild‐type leaves treated with different titers of Pst DC3000 (AvrRpm1). Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 4; 3–9 leaves each).
Quantification of lignin content in wild‐type and rpm1‐3 rps2‐101c leaves treated with avirulent bacteria. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 4; 3–9 leaves each).
Data information: Twelve‐day‐old seedlings were flood‐inoculated with
P. syringae at 10
8 cfu/ml in (A, C). Six‐week‐old leaves were syringe‐infiltrated with
P. syringae at 10
8 cfu/ml in (B, D, F) and at the indicated titers in (E). Significant differences are indicated by different letters (Tukey's HSD test;
P <
0.05) and by asterisks (
t‐test; *
P <
0.05; **
P <
0.01; ***
P <
0.001). Experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
hrcC
−,
Pst DC3000
hrcC
−; DC3000,
Pst DC3000;
AvrRpm1,
Pst DC3000 (
AvrRpm1);
AvrRpt2,
Pst DC3000 (
AvrRpt2); dpi, days post‐inoculation; IS, infected site; UIS, uninfected site.