Figure 4.
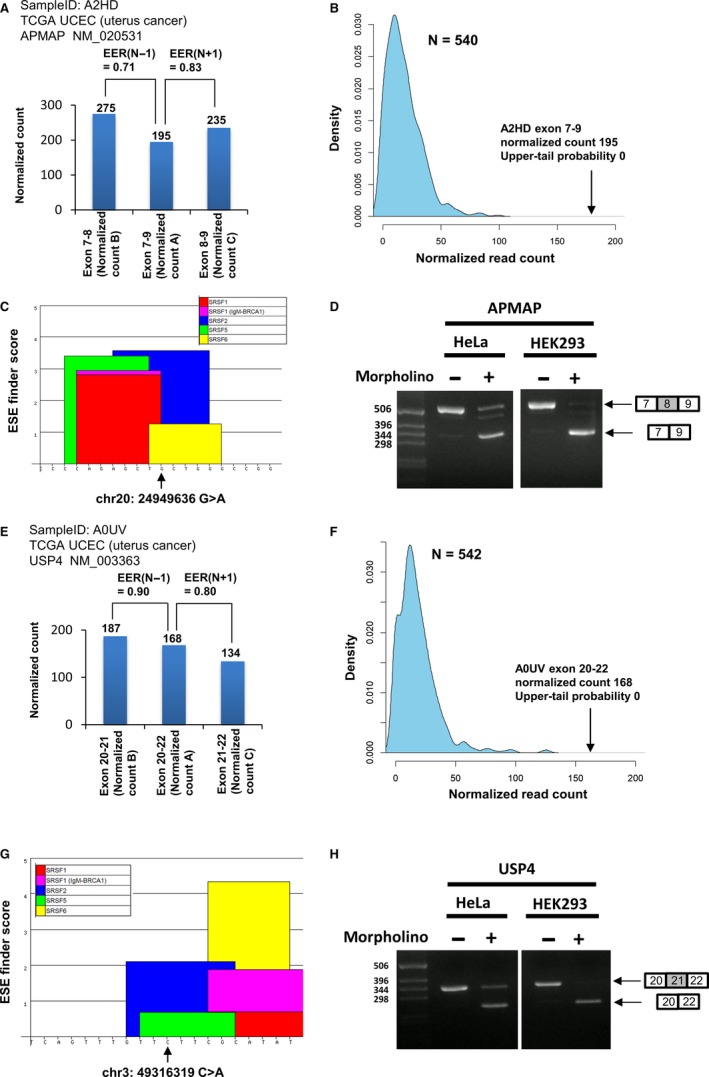
Examples of ESE‐disrupting variants identified. A, Normalized read counts of each exon‐exon junction around the APMAP gene somatic variant in the uterus cancer A2HD sample. B, Estimated normalized count distribution of exons 7‐9 without variants in APMAP in TCGA UCEC project samples (N = 540) determined by kernel density estimation. C, ESE finder graphical result of exon 8 somatic variant (chr20: 24949636 G>A) in the APMAP gene from sample A2HD. D, PCR‐based splicing pattern analysis by morpholino oligos targeting an ESE‐disrupting variant in exon 8 of the APMAP gene in HeLa and HEK293 cell lines. E, Normalized read counts of each exon‐exon junction around the USP4 gene somatic variant in the uterus cancer A0UV sample. F, Estimated normalized count distribution of exons 20‐22 without variants in USP4 in TCGA UCEC project samples (N = 542) determined by kernel density estimation. G, ESE finder graphical result of exon 21 somatic variant (chr3: 49316319 C>A) in the USP4 gene from sample A0UV. H, PCR‐based splicing pattern analysis by morpholino oligos targeting an ESE‐disrupting variant in exon 21 of the USP4 gene in HeLa and HEK293 cell lines
