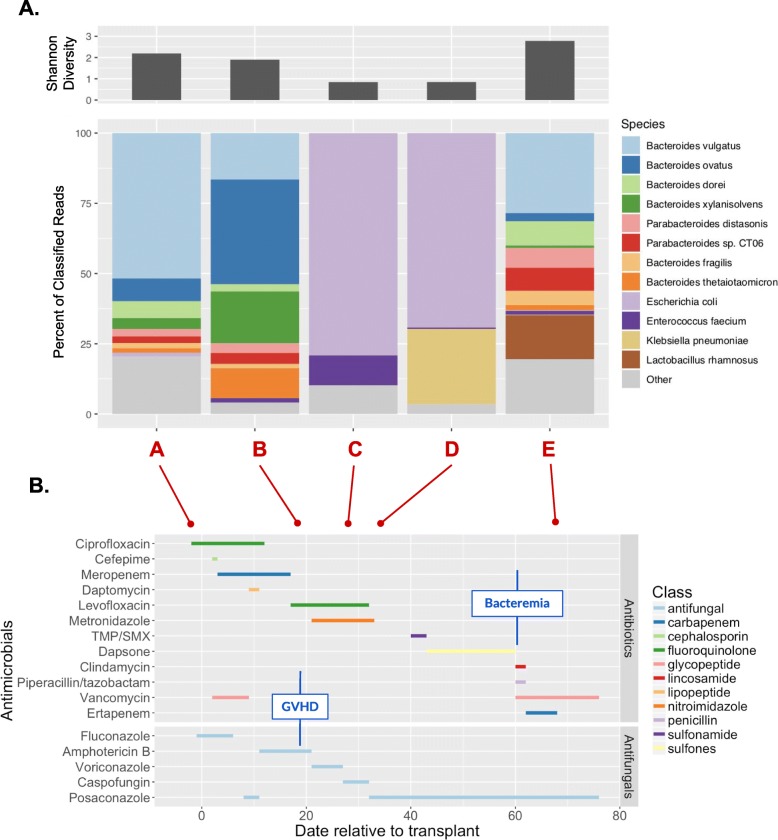
Fig. 1.
A Shannon diversity and composition of the intestinal microbiome of the study subject across five time points over the course of HCT obtained from species-level taxonomic classification of conventional short-read samples. Each bar represents one stool sample, where colors represent different species and thickness indicates relative readcount attributed to that species within the sample (proportion of total reads classified to the species level). “Other” represents species comprising < 2% readcount. Microbial diversity decreases to a period of domination by E. coli (time points C and D) followed by recovery of diversity (time point E). B Clinical time course of the study subject. The x-axis denotes number of days after transplantation. Dates on which a stool sample was collected are marked by red dots. Each row portrays the start and end date of administration of an antibiotic (antibiotic class indicated by the color of the line). The timing of GVHD onset and bloodstream infection (bacteremia) are marked