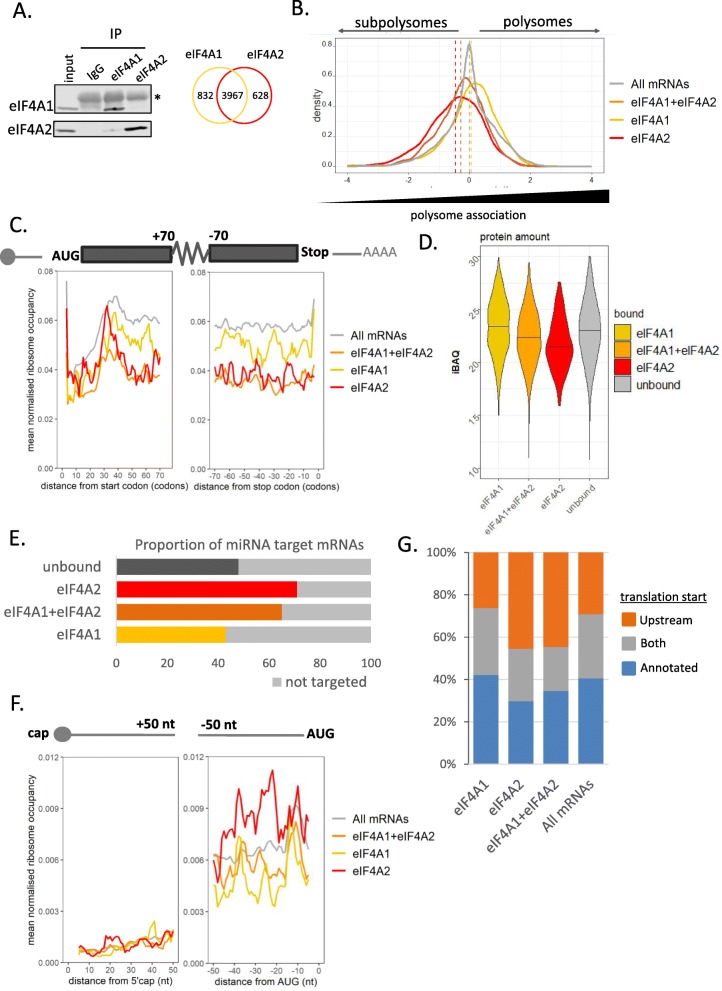
Fig. 2.
eIF4A2 represses translation at initiation. a Western blot demonstrates specificity of immunoprecipitation for each protein from a representative experiment. Input represents 10% of lysate used in IP. Asterisk denotes non-specific signal from IgG. Venn diagram showing numbers of mRNAs significantly (FDR < 0.05) enriched over input in the respective endogenous RIP-Seq (n = 3). b Differential association with polysomes of mRNAs bound to one of the two proteins or both compared to all mRNAs identified in the RIP-Seq experiment. Relative distribution of mRNAs on sucrose density gradients was calculated from RNA-Seq analysis of the subpolysomal and polysomal fractions in a separate experiment (n = 4) by subtracting counts per million between the two fractions. Significance calculated using Dunn’s test with Bonferroni’s correction. c Differential ribosome occupancy of eIF4A2- and eIF4A1-bound messages. Ribosome profiling was performed in HEK293 lysates (n = 3). Ribosome occupancy for each mRNA at each nt position is calculated as the number of ribosome footprints normalized to the mRNA abundance (transcripts per million—TPM). Shown is the mean number of normalized ribosome footprints 75 codons downstream of the AUG and upstream of the STOP codon. d iBAQ—intensity-based absolute quantification [48]—of protein abundance in control conditions in pulsed SILAC for bound mRNAs. e Proportions of mRNAs bound by eIF4A1 and eIF4A2 predicted to be miRNA targets by the Targetscan algorithm. f eIF4A2-bound mRNAs have increased ribosome occupancy in the last 50 nt, but not in the first 50 nt of the 5′UTR. The RPF coverage was normalized for the abundance of the mRNAs (TPM). g Translation of the main AUG start codon is repressed by activation of uORFs in eIF4A2-bound mRNAs. Global translation initiation sequencing (GTI-seq) data from Lee et al. [49], also conducted in HEK293 cells, was used to assess the translation from uORFs in the groups of mRNAs bound by either eIF4A1, eIF4A2, or both. The stacked bars represent the proportions of the groups of mRNAs with active translation from the annotated translation start site, upstream start sites, or both