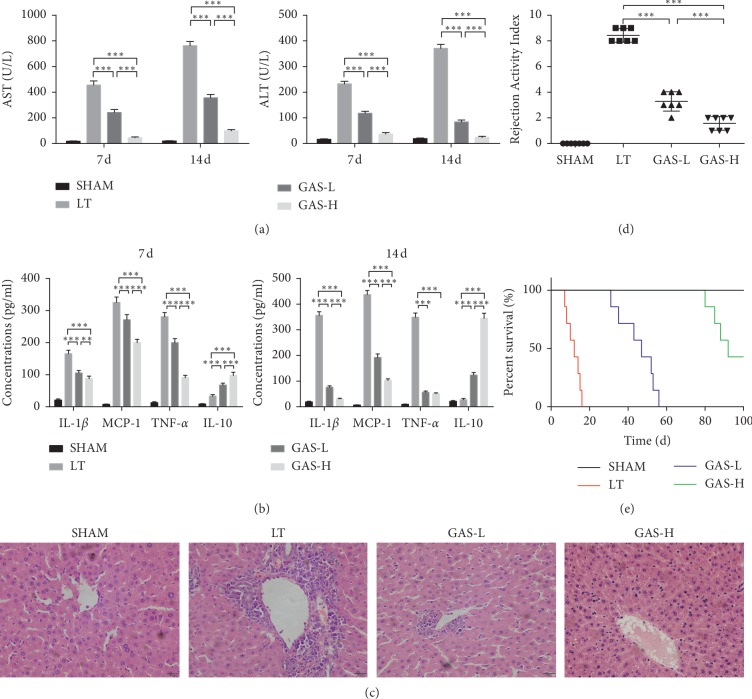
Figure 2.
GAS ameliorates inflammatory response of liver transplantation and promotes survival time in rats. (a) Serum concentrations of ALT and AST in GAS treatment groups were significantly decreased after LT (n ≥ 5, ∗∗∗P < 0.001). (b) Inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, MCP-1, TNF-α, and IL-10 were significantly decreased in GAS treatment groups (n ≥ 5, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001). (c) Hematoxylin and eosin staining for observing the pathological damage. Visible focal necrosis and vacuolization of the liver parenchyma with lymphocyte infiltration were observed in the LT group, while GAS treatment groups had a normal architecture (magnification: ×400). (d) Banff schema for Rejection Activity Index (RAI) 14 d postoperatively. GAS treatment groups were judged as nondeterministic acute rejection (n ≥ 5, ∗∗∗P < 0.001). (e) Rat survival time was observed and analyzed using the log-rank test. Values represent mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments.