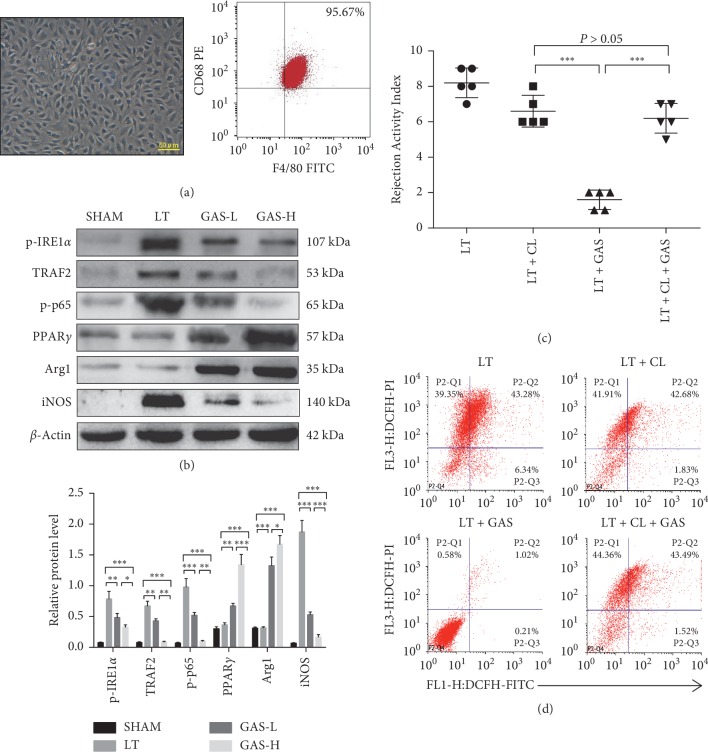
Figure 5.
GAS acts mainly on intrahepatic macrophages in liver transplantation. (a) Intrahepatic macrophages were isolated from liver tissues 14 d postoperatively in each group. Intrahepatic macrophages mostly showed long spindle-shaped growth after cell attachment (magnification: ×400, scale bars: 50 μm), and the purity of macrophages was over 95% with flow cytometric analysis. (b) Western blot was performed using intrahepatic macrophages collected 14 d postoperatively. The expression of p-IRE1α, TRAF2, p-p65, and iNOS proteins was decreased, and the expression of PPARγ and Arg1 was increased (n ≥ 5, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001). (c) The LT group underwent liver transplantation surgery. LT + GAS group recipient rats were injected with 100 mg/kg GAS via the caudal vein daily for 1 week after surgery. LT + CL group donor rats were injected with clodronate liposomes (CLs; 10 mg/kg) via the caudal vein to destroy intrahepatic macrophages 24 h prior to surgery. LT + CL + GAS group donor rats were injected with clodronate liposomes (CLs; 10 mg/kg) via the caudal vein to destroy intrahepatic macrophages 24 h prior to surgery, and recipient rats were injected with 100 mg/kg GAS via the caudal vein daily for 1 week after surgery. All rats underwent analysis to determine the Rejection Activity Index (RAI) score 14 d postoperatively (n ≥ 5, ∗∗∗P < 0.001). (d) The groups were the same as described in (c). The flow cytometric analysis of ROS production in liver cells was done using CM-H2-DCFDA and PI double staining. Values represent mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments.