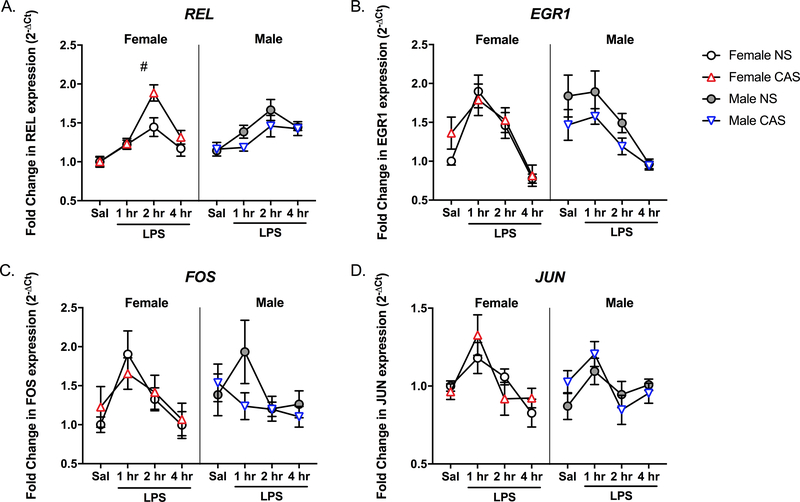
Fig 4. CAS leads to priming of hippocampal REL gene expression in female rats.
Male and female rats of NS or CAS backgrounds received a single systemic injection of saline or LPS in adulthood to unmask potential immune priming due to stressor exposure (n = 5–7/group). Targeted qPCR experiments confirmed that LPS led to a significant mRNA induction of all four NFκB-related genes (p<0.001) in the hippocampus. While there was no main effect of CAS, sex and CAS interacted such that CAS exaggerated the hippocampal mRNA expression of A) REL in female (p=0.049, #), but not male, rats (p>0.05). B) Similarly, sex and CAS interacted such that CAS males displayed a trend toward lower EGR1 expression compared to non-stressed males (p=0.056). CAS did not impact the mRNA expression of C) FOS or D) JUN in the hippocampus of either males or females (p>0.05). Data are presented as mean fold change ± SEM. # main effect of CAS within females.