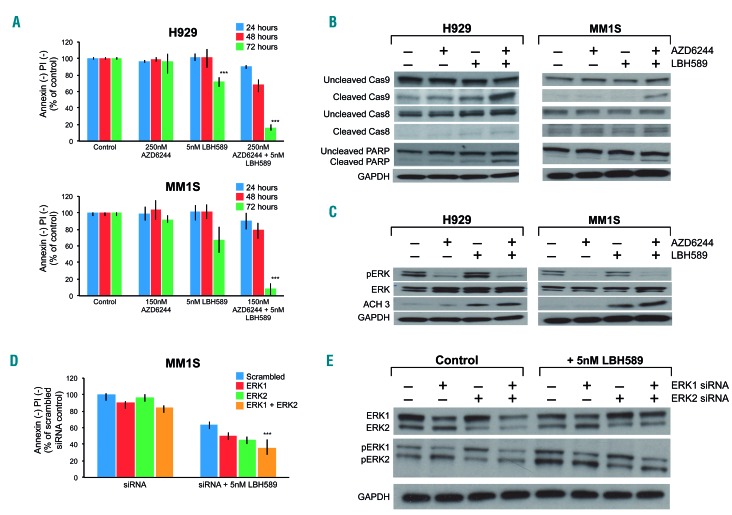
Figure 2.
MEK + histone deacetylase inhibition drives synergistic apoptosis in multiple myeloma cell lines and inhibits target proteins. (A) Flow cytometric cell viability of the RAS mutant human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines H929 and MM1S measured as the proportion of annexin−/propidium iodide (PI)− cells, after 24, 48 and 72 h of treatment with AZD6244 and LBH589 at the indicated doses. Viability is shown as percent of control on the Y-axis. (B,C) H929 and MM1S were treated with AZD6244/LBH589 for 24 h, then whole-cell lysates were separated using sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and subjected to western blotting for the indicated proteins. (D) MM1S was electroporated with scrambled siRNA, ERK1, ERK2 siRNA or the combination, then left untreated or treated with 5 nM LBH589. At 72 h, cell viability was assessed using flow cytometry by analyzing the proportion of annexin−/PI− cells, shown as percent of control on the Y-axis. (E) Whole-cell lysates from these cells were separated using SDS-PAGE and subjected to western blotting to confirm ERK1 and ERK2 silencing. Error bars represent the standard error of mean of triplicate experiments. Differences between groups were calculated with the Student t test. **P<0.001. All experiments were performed in triplicate.