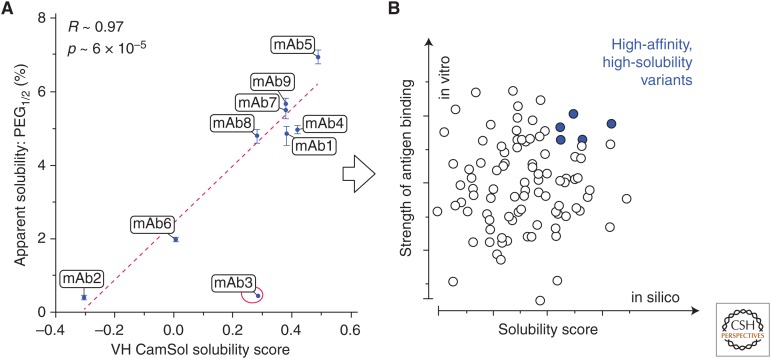
Figure 1.
(A) Scatterplot of the measured apparent solubility (expressed as the value of PEG1/2) of a directed-evolution-derived mAb library (Sormanni et al. 2017) as a function of the intrinsic CamSol solubility score calculated from the sequences of the heavy chain variable domain (VH) only, as the vast majority of mutations are found there. Regression lines, reported Pearson's coefficients of correlation (R), and corresponding p values (p) were calculated by excluding the outlier point circled in red (mAb3). (B) The computational prediction in A enabled the identification of the most soluble mAbs. Therefore, the screening of antibodies derived from an in vitro discovery experiment (e.g., phage display) may be performed using two parameters: (1) the measured binding strength (e.g., binding affinity or off-rate on the y-axis), and (2) the predicted solubility score calculated from the sequence (e.g., the CamSol-intrinsic solubility on the x-axis). The latter is readily computed from the amino acid sequence, thus enabling the selection of lead antibodies with high affinity and solubility from the very early stages of antibody discovery (adapted from Sormanni et al. 2017).