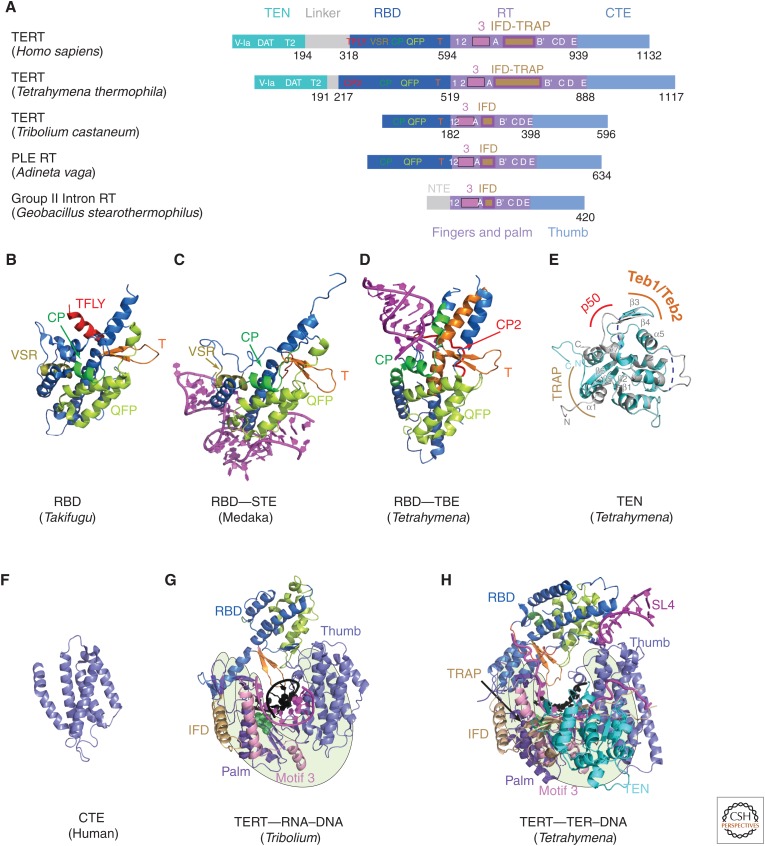
Figure 3.
TERT domains and structures. (A) Schematics comparing domains of reverse transcriptases (RTs) from human telomerase, Tetrahymena telomerase, Tribolium castaneum telomerase, Penelope-like element (PLE; Adineta vaga), and Group II intron (Geobacillus stearothermophilus). Domains and conserved motifs are aligned using the RT domains. Note that Tribolium “TERT” is more similar to the A. vaga PLE RT than to the true TERTs from human and Tetrahymena. Crystal structures (B–G) of (B) Takifugu rubripes RBD (PDB: 4LMO), (C) medaka RBD–STE complex (PDB: 4O26), (D) Tetrahymena RBD–template boundary element (TBE) complex (PDB: 5C9H), and (E) free Tetrahymena telomerase amino-terminal domain (TEN) (PDB: 2B2A, cyan) superimposed with cryo-EM structure of TEN in Tetrahymena telomerase holoenzyme (PDB: 6D6V) (gray). Regions interacting with p50, TEB, and TRAP are indicated. Blue dashed lines represent the missing loops in the crystal structure. (F) Human carboxy-terminal element (CTE) (PDB: 5UGW) and (G) Tribolium TERT with an RNA–DNA hairpin mimicking a template–DNA duplex (PDB: 3KYL). (H) Cryo-EM structure of Tetrahymena TERT–TER with template–DNA duplex (PDB: 6D6V). TRAP is mostly covered by TEN, so is difficult to see in this view. The TRAP and TEN domains are unique to TERT, whereas motif 3 and IFD are found in closely related RTs from group II introns and PLEs. For G and H, the polymerase “hand” view is shown.