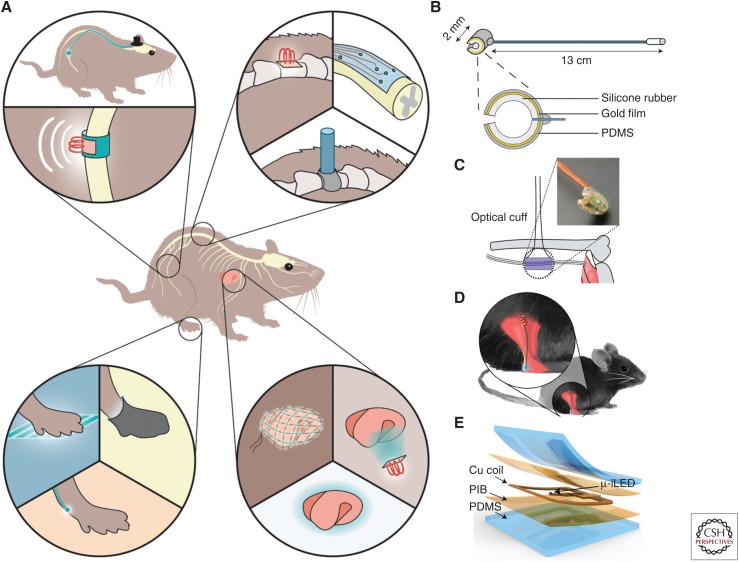
Figure 2.
Light delivery methods for optogenetic studies in awake, freely moving rodents. (A) Schematic illustration of super soft and flexible optic cuff for optogenetic neuromodulation of large peripheral nerves, the spinal cord, nerve endings, and internal organs. (Panel based on data in Montgomery et al. 2016.) (B) Illustration of an optic fiber-based optic cuff implant for sciatic nerve stimulation in awake, freely moving mice. (Panel reprinted from Michoud et al. 2018 courtesy of IOP Publishing in conjunction with Creative Commons Licensing.) (C) Illustration of a micro LED-based optic cuff implant for sciatic nerve stimulation in anesthetized mice. (Panel based on data in Llewellyn et al. 2010.) (D) Illustration of a micro LED implant for illumination of sciatic nerve endings in awake, freely moving mice. (Panel reprinted from Montgomery et al. 2016 with permission from The American Association for the Advancement of Science © 2016.) (E) Illustration of a super soft, micro LED-based optoelectronic device for illumination of sensory nerve endings on the bladder in awake, freely moving mice. (Panel reprinted from Samineni et al. 2017a courtesy of Scientific Reports in conjunction with Creative Commons Licensing.)