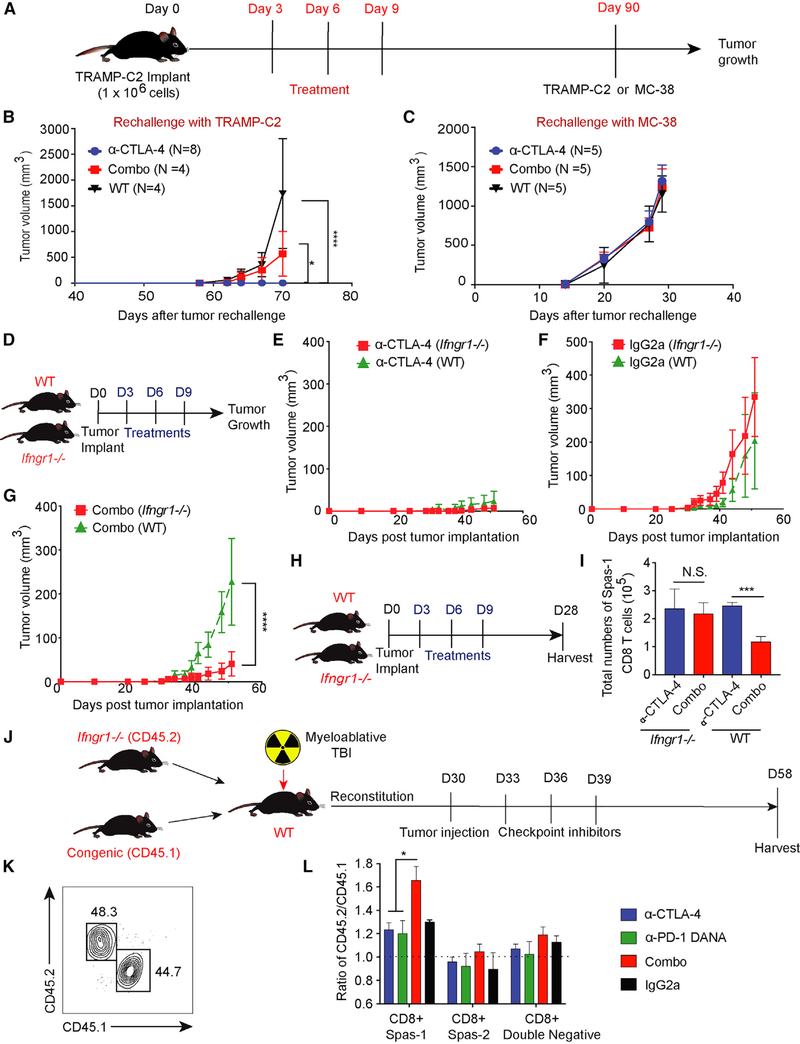
Figure 6. Effective Anti-tumor Response with Dual Checkpoint Blockade Is Restored when T Cells Are Made Unresponsive to IFN-γ.
(A) Eight-week-old C57BL/6j mice were challenged with TRAMP-C2 tumor on day 0 and treated with checkpoint inhibitors on days 3, 6, and 9. Ninety days after tumor implantation, tumor-free mice from CTLA-4 blockade or combination-treatment groups were subsequently re-challenged with either the TRAMP-C2 or MC-38 tumor model. Aged sibling mice without prior tumor challenge were used as control mice.
(B) Mice were re-challenged with TRAMP-C2 tumors.
(C) Mice were re-challenged with MC-38 tumors. To allow a sufficient number of tumor-free mice, each treatment group consisted of 30–45 mice. The numbers of tumor-free mice for re-challenge are labeled correspondingly.
(D) Age-and gender-matched WT or Ifngr1−/− C57BL/6j mice were implanted with tumors at day 0 and treated with checkpoint inhibitors on days 3, 6, and 9.
(E) Comparison of tumor growth curves in the CTLA-4-blockade treatment.
(F) Comparison of tumor growth curves in the isotype-control treatment.
(G) Comparison of tumor growth curves with the combination-blockade treatment.
(H) WT or Ifngr1−/− mice were treated with checkpoint blockade and harvested at day 28.
(I) Total numbers of CD8+ Spas-1 T cells.
(J) WT mice were myeloablated (10.5 Gy) and given an adoptive transfer of bone marrow cells from CD45.2 Ifngr1−/− and CD45.1 Pepc congenic WT mice at a 1:1 ratio. Chimera mice were subsequently implanted with TRAMP-C2 tumors and treated with checkpoint inhibitors on days 33, 36, and 39 after bone marrow transplant.
(K) Mice underwent tail bleeding and were checked for chimerism 30 days after bone marrow transplantation.
(L) Tumor-draining lymph nodes were harvested on day 58. Different CD8+ subsets were pre-gated on flow cytometry and investigated for chimerism.
Experiments included eight (D–G) or five (H and I) mice per group. For (J) and (L), each treatment consisted of five chimera mice per group for a total of 20 chimera mice in these experiments. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with a post hoc test (B–G) or by one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey test (I and L). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Data are presented as mean ± SE. See also Figure S6.