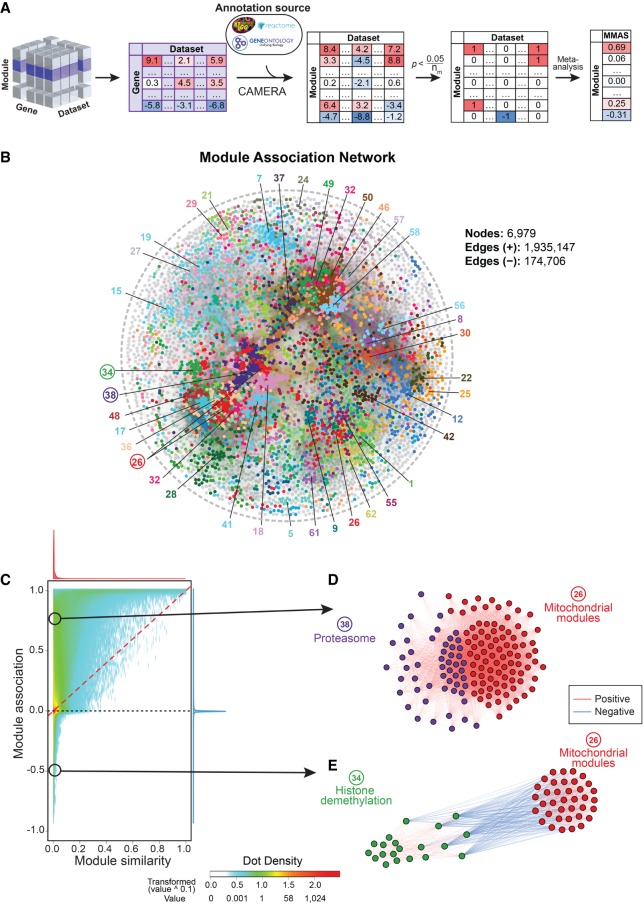
Figure 5.
Module-Module Association Determination (M-MAD) reveals module connections. (A) Scheme of the M-MAD methodology in detecting module connections. Intermediate results of G-MAD for all modules are further processed and used as the basis of M-MAD. The −log10(P) values of G-MAD for the target module against all genes in each data set are used as the gene statistic for the module, and connections between the target module and all modules are calculated using CAMERA. The results are then meta-analyzed by taking the sample sizes and inter-gene correlations of all data sets to compute the module-module association score (MMAS) between modules. (B) Module association network showing the connections across all modules. Colors of nodes represent the modules defined in the global module similarity network in Figure 1B. Module clusters with respective colors are identified and labeled. Modules used as examples in the following figure panels are highlighted with a circle. (C) Comparison of pairwise module connections derived from module similarities in Figure 1B and associations (from M-MAD) in Figure 5B. A red dashed line is plotted when the pairwise module similarity equals association. The distributions of module similarity and association scores are illustrated in the top and at the right of the plot and are colored in red and blue, respectively. Two examples of novel module connections are encircled. (D,E) Subnetworks showing the association between mitochondrial and proteasomal modules (D), and mitochondrial and histone demethylation modules (E). Edge colors indicate the significance of module connections, with red as positive and blue as negative.